Country Code
What is Country Code?
A country code is a unique identifier usually assigned to a country or territory. These codes, comprising abbreviations or numbers, are the standard means to identify countries in various spheres of life, from international trade and data processing to telecommunications and Internet.
ISO 3166-1 Alpha-2
ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes are well-known country code systems. In 1974, the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) developed these two-letter codes for the first time. They provide the foundation for other uses of country codes and are widely used in data processing, international trade, and internet domain names.
The ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes are used in the ISO 4217, the standard currency codes. Every country has an allocated 3-letter code derived from their ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code and serves as a standardized way of representing currencies in inter-country transactions. Moreover, website country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) adopt ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes, thus making the link between a country and its online visibility obvious.
International Subscriber Dialing (ISD) Code
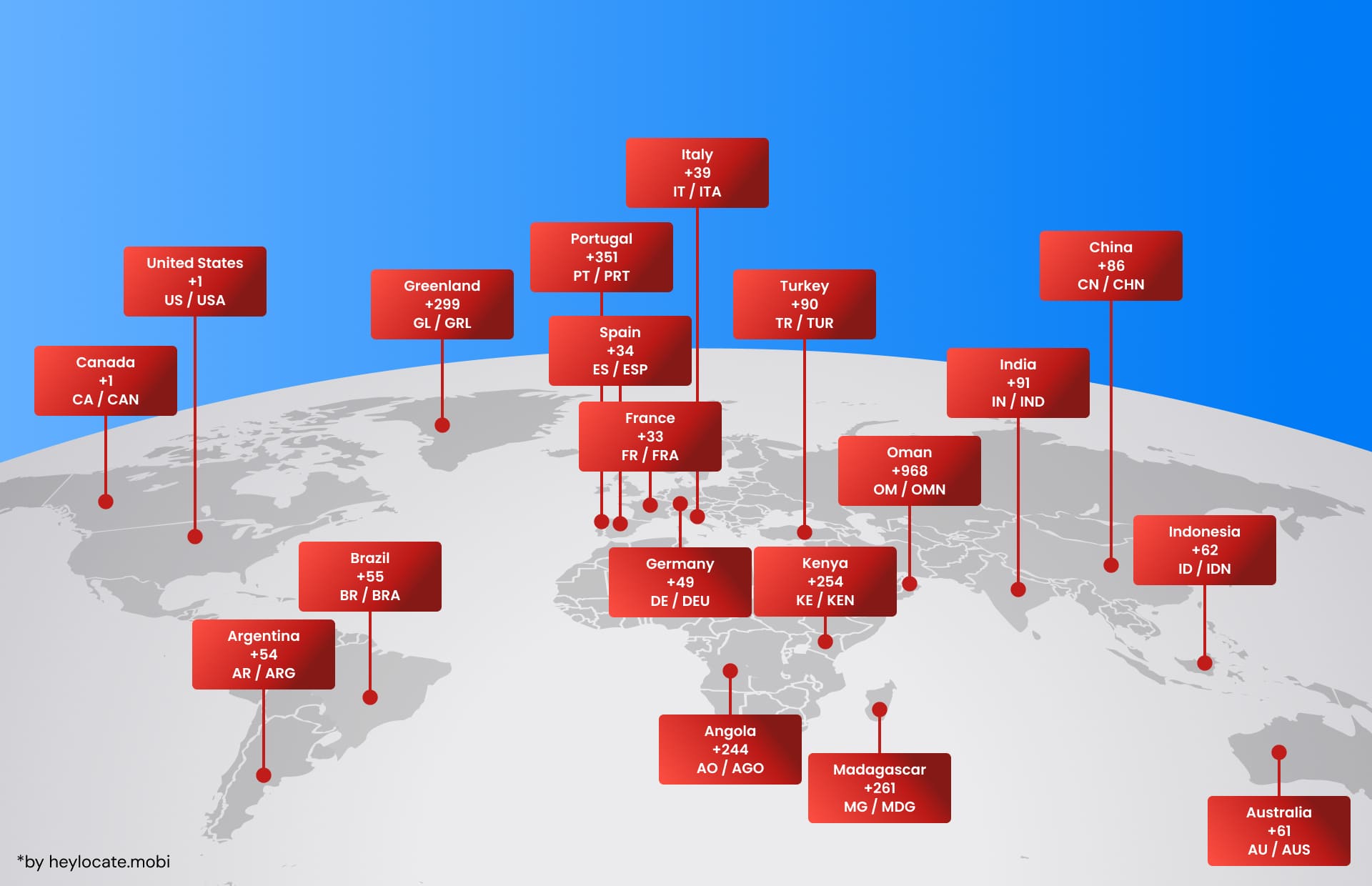
In telecommunications, country codes are very important because they are responsible for international calls. The International Subscriber Dialing (ISD) code, the country calling code, is the numerical prefix that goes before a phone number to indicate the country of destination. These codes serve for effective communication between countries and are conformed to international standards.
The ITU (International Telecommunication Union) has adopted special recommendations, such as ITU-T recommendations E.123 and E.164, as the standards for country codes. These standards make communication networks across the globe uniform and compatible. In addition, autonomous telephone authorities of countries with own telephone numbering plans should meet these standards when allocating their ISD codes.
European Union
Inside the European Union (EU) ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes are applied with slight alterations to the member states. For example, the Greek ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code is EL, which originates from the country’s official name, “Hellenic Republic,” but the UK code is UK. These amendments mean that the country codes are compatible with the official names or abbreviations used inside the EU.
Other Country Code System
Furthermore, ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes and their uses are not the only country code systems that are employed across industries. These codes are tailored to fulfill certain purposes and are used in sports, transportation, broadcasting, and many other areas.
- FIFA Trigramme codes: Utilized by FIFA to signify the nations in soccer.
- FIPS 10-4 codes (withdrawn): Before, the US authorities used it for different functions.
- World Area Codes (WAC): Three-digit codes that are employed by the U.S. Department of Transportation for aviation, transportation, and anything else.
- GOST 7.67 codes: Cyrillic country codes invented by the former Soviet Union.
- ICAO codes: Given by the ICAO to recognize aircraft as well as airport places.
- IOC three-letter codes: Used by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) in sports to identify country abbreviations.
- ITU codes: It is called the International Telecommunication Union and used for telecommunication tasks, such as mobile networks radio stations and broadcasting.
- Maritime identification digits: For ship-to-ship communication use in maritime mobile radio transmitting.
- License plates: Many countries use country codes to denote country of origin on license plates.
- NATO codes (transitioned): Originally, for military and administrative use of NATO.
- UNDP trigram country codes: Used by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) for statistical and analytical purposes.
- WIPO and WMO country codes: Utilized by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and World Meteorological Organization (WMO) for international cooperation and data exchange, respectively.
- UIC Country Codes: Appointed by the International Union of Railways (UIC) to give railways and railway operators an identification code.
| System | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 3166-1 Alpha-2 | Two-letter country codes | US (United States), FR (France), JP (Japan), DE (Germany), IT (Italy), ES (Spain), BR (Brazil) |
| International Dialing (ISD) | Country calling codes | +1 (United States), +33 (France), +81 (Japan), +351 (Portugal), +34 (Spain), +39 (Italy), +49 (Germany), +39 (Brazil) |
| European Union (EU) | EU-specific codes | EL (Greece), UK (United Kingdom) |
| Other Country Code Systems | Various purposes | FIFA: BRA (Brazil), ICAO: EGLL (Heathrow Airport), IOC: USA (United States) |
References
- ISO 3166-1 alpha-2
- ISO 4217
- International Telecommunication Union
- European Union
- FIFA Trigramme codes
- FIPS 10-4 codes
- World Area Codes
- GOST 7.67
- ICAO codes
- IOC three-letter codes
- ITU codes
- Maritime identification digits
- License plates
- NATO codes
- UNDP trigram country codes
- WIPO country codes
- WMO country codes
- UIC Country Codes