User Interface (UI)
What is User Interface (UI)?
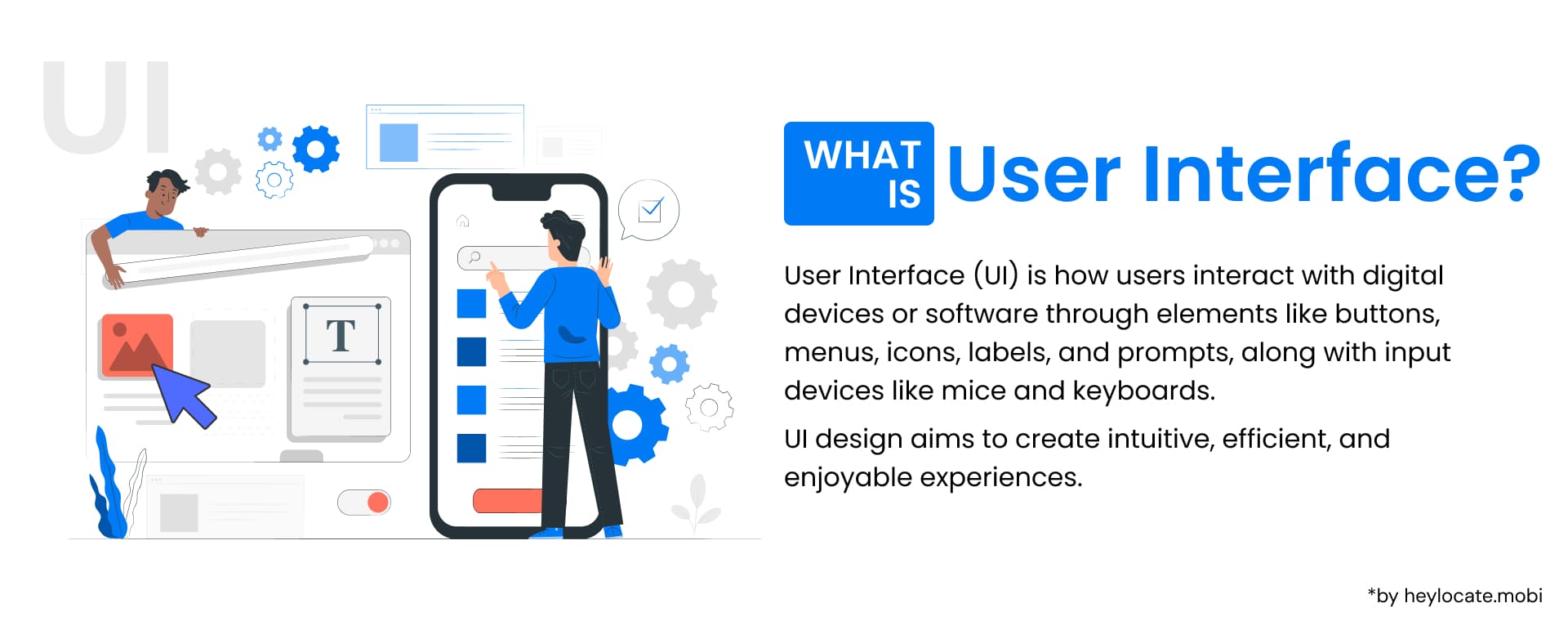
User Interface (UI) is the point of interaction between humans and machines. It is how users communicate with software, applications, websites, and other digital systems. The primary goal of UI is to facilitate effective operation and decision-making by presenting information and functionality in an intuitive and user-friendly manner.
Components of UI
UI encompasses various components, including:
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): The physical input and output hardware that enables users to interact with the machine. This includes components such as keyboards, mice, touchscreens, and displays.
- Sensory UI Layers: Emerging technologies that expand the possibilities of UI. These include brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), haptic feedback, and virtual reality.
User Interface Design Principles
- Ergonomics and Usability: Optimizing the design of the interface for human use by considering human factors such as physical abilities, cognitive capabilities, and user preferences. Usability engineering involves the systematic evaluation and improvement of the user experience.
- Multimodal and Composite Interfaces: Multimodal interfaces combine multiple input and output modalities to enable more natural and intuitive interaction. Composite user interfaces (CUIs) integrate different UI technologies into a cohesive whole.
Understanding UI Terminology
- UI: Refers specifically to the interaction space between humans and machines, encompassing both physical and digital elements.
- HMI: Focuses on the physical hardware that enables interaction (e.g., keyboards, touchscreens).
- HCI: The broader term encompassing the study and design of interfaces between humans and computers, including both hardware and software aspects.
Types of User Interfaces
| Type of UI | Description | Example | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphical User Interface (GUI) | Most common type, uses visual elements like icons, menus, and windows. | Desktop applications, web browsers, mobile apps | General purpose computing, information access, content creation |
| Text-Based User Interface (TUI) | Relies on text commands and responses for interaction. | Command-line interfaces (CLI) | System administration, power user tasks, scripting |
| Voice User Interface (VUI) | Enables interaction through spoken commands and natural language processing. | Virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa), smart speakers | Voice-activated controls, hands-free interaction |
| Human-Machine Interface (HMI) (Technically a UI Component) | Focuses on the physical hardware used for interaction. | Keyboards, mice, touchscreens, joysticks | Provides physical touchpoints for user input and system feedback |
| Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) (Advanced Interface) | Enables communication between the brain and a computer system. (Still under development) | Research prototypes for medical applications, assistive technologies | Direct thought control for individuals with disabilities |
| Qualia Interface (Advanced Interface) | Theoretical concept aiming to create interfaces that convey subjective experiences. | Not currently implemented | Potential future applications in emotional communication and immersive experiences |
References
- Graphical user interface – Wikipedia
- What is user interface (UI)? Definition from SearchAppArchitecture
- What is User Interface (UI)? (Types & Features) | BrowserStack
- What Is A User Interface & What Are The Key Elements?
- User Interface Design Basics | Usability.gov
- What Is A User Interface? Definition & Best Practices For UI Design
- What is User Interface (UI)? Definition, Examples and Best Practices – Trymata
- What is User Interface (UI)? | Pendo.io