Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
What is CDMA?
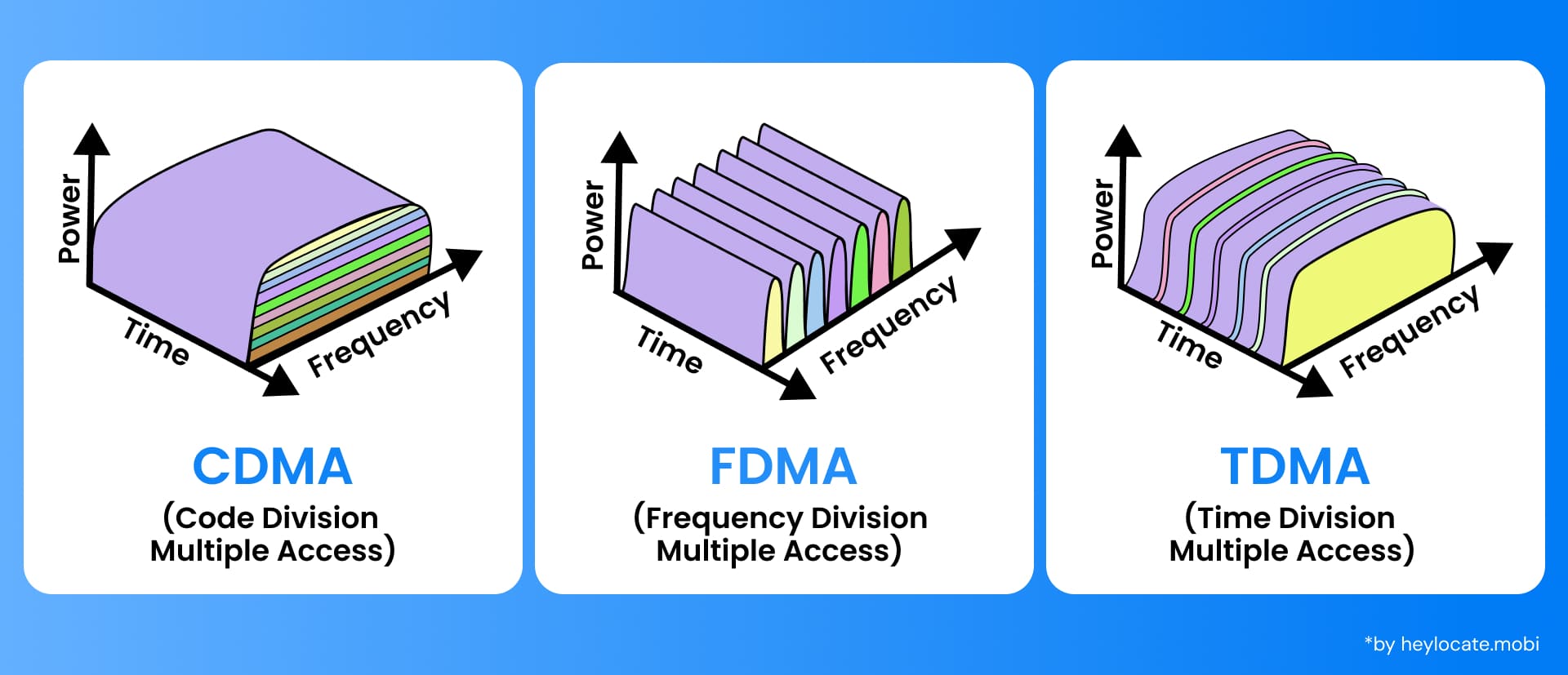
Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA) is an important channel access method employed in telecommunications. Unlike its counterparts such as Time-Division Multiple Access (TDMA) or Frequency-Division Multiple Access (FDMA), which allocate distinct time slots or frequency bands to individual users, CDMA facilitates multiple transmitters to concurrently transmit information over a singular communication channel. This distinctive capability to share the same frequency band without encountering interference renders CDMA indispensable across various domains, including mobile phone standards, GPS systems, and satellite communications.
Core Technologies Driving CDMA
At the core of CDMA technology lies spread spectrum technology, which efficiently distributes frequencies among users. This technique disperses the signal energy over a broad bandwidth, reducing interference and enhancing system robustness. A distinguishing coding scheme, a spreading code or sequence, discerns user signals, enabling their separation at the receiver.
These codes possess unique mathematical properties ensuring signal independence. User information undergoes multiplication by the spreading code, spreading across a comprehensive frequency range. The same code is subsequently employed at the receiver to despread the signal and isolate the intended user’s information.
Bandwidth Optimization
CDMA optimizes available bandwidth by capitalizing on the entire frequency range allocated for communication. In contrast to FDMA, where each user is assigned a dedicated frequency band, CDMA enables all users to transmit simultaneously, utilizing the entire frequency spectrum. This efficient bandwidth utilization accommodates a higher capacity of concurrent users, making CDMA an appealing choice for communication systems characterized by high user density.
Modulation Techniques and Applications
Various modulation schemes are employed in CDMA to bolster system robustness and efficiency. These schemes determine the method by which information is encoded onto the carrier signal for transmission.
Commonly utilized schemes encompass:
| Modulation Technique | Description | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPSK (Binary Phase-Shift Keying) | Modulates the carrier signal’s phase to transmit data, with two phases representing binary 0 and 1 | Simple and robust against noise Less bandwidth-efficient compared to higher-order schemes | Satellite communication RFID and NFC Low-bandwidth applications |
| QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) | Combines amplitude and phase modulation to transmit multiple bits per symbol, allowing for higher data rates | Higher spectral efficiency More complex, requiring better signal-to-noise ratio | Cable modem and broadband Digital TV broadcasting High-speed internet services |
| OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) | Divides the available bandwidth into multiple subcarriers, each carrying a part of the data, to improve efficiency and reduce interference | Higher spectral efficiency More complex, requiring better signal-to-noise ratio | 4G LTE and 5G mobile networks Wireless and broadband internet Digital broadcasting (DAB, DVB) |
Application of CDMA Across Domains
CDMA has garnered widespread utilization across various domains, reshaping communication landscapes and enhancing navigation capabilities.
Mobile Phone Standards and Evolution
CDMA has significantly contributed to the evolution of mobile phone standards. Early standards such as IS-95 (cdmaOne) offered enhanced capacity and call quality in comparison to analog systems. The subsequent evolution to CDMA2000 introduced higher data rates and laid the groundwork for 3G standards like W-CDMA. However, with the advent of 5G, mobile network operators are phasing out CDMA in favor of newer technologies.
GPS and Satellite Communications
CDMA finds applications in Global Positioning System (GPS) technology and satellite communications.
- GPS: CDMA enables simultaneous signal transmission from multiple satellites, ensuring accurate positioning information for GPS receivers worldwide.
- Satellite Communications: CDMA optimizes bandwidth, allowing multiple users to transmit data concurrently, ensuring efficient communication.
Spread Spectrum and Modulation Process
In the CDMA modulation process, a CDMA signal is created by multiplying the user’s information signal with a spreading code. This action spreads the signal’s energy across a broader frequency range and enhances resilience against interference.
The selection of spreading code and modulation scheme is customized to suit the particular system requirements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Challenges in CDMA Systems
One of the challenges in CDMA systems is asynchronous transmission. It necessitates the use of pseudo-random sequences to synchronize received signals and distinguish between users.
Additionally, the near-far problem arises when users are at varying distances from the base station, leading to discrepancies in signal strengths. CDMA systems mitigate this issue through power control techniques.
Effective signal strength control is imperative in CDMA systems to prevent interference and optimize system capacity. CDMA transmitters employ power control algorithms to regulate transmission power based on received signal strength. This minimizes interference and enhances overall system efficiency.
References
- Torrieri, Don (2018). Principles of Spread-Spectrum Communication Systems, 4th ed.
- Stuber, Gordon L. (2017). Principles of Mobile Communication, 4th ed.
- Robert Price (28 July 1982). “Oral-History: Claude E. Shannon”. Engineering and Technology History Wiki.
- Code-division multiple access – Wikipedia
- What is CDMA (Code-Division Multiple Access)?
- What is CDMA and How Does it Work?