Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)
What is GNSS?
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) is a constellation of satellites that furnish positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) data globally. These systems employ a network of satellites encircling the Earth, emitting signals received by GNSS receivers on the ground. The receiver can ascertain its precise location by calculating signal travel time to the receiver and the known satellite positions.
Distinction between Satellite Navigation Systems and GNSS
Distinguishing between Satellite Navigation Systems and GNSS, the former denotes individual systems like GPS, while the latter encompasses multiple global and regional systems. GNSS includes GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), BeiDou (China), and Galileo (Europe), ensuring global coverage and redundancy for accurate PNT information accessibility.
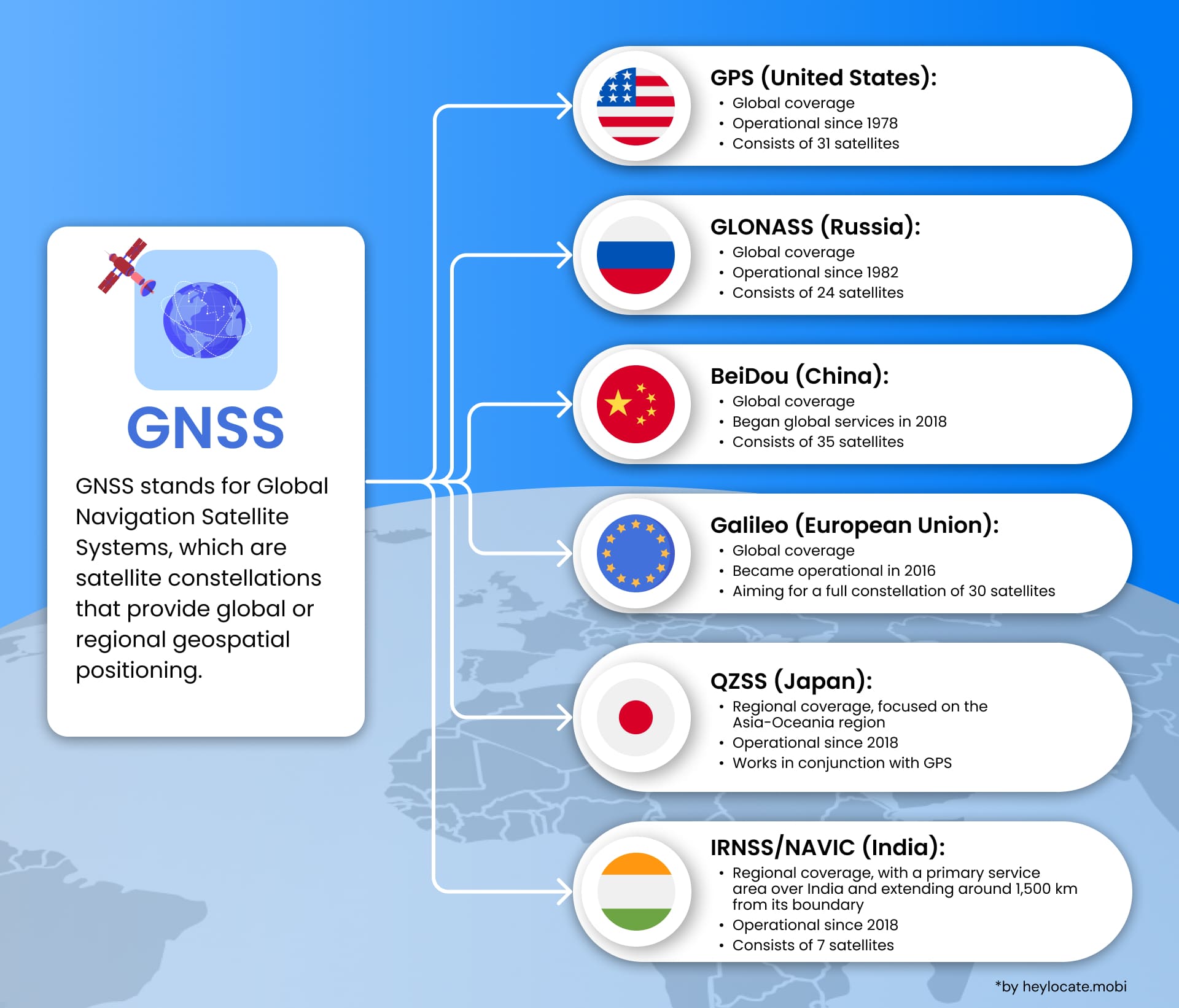
Overview of Operational Global Systems
The primary operational global systems within the GNSS framework are GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo:
| Operational Global Systems | Origin | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GPS (Global Positioning System) | United States | The most well-known and widely used GNSS system, developed and operated by the United States Department of Defense. Provides precise positioning and navigation data through a network of satellites that orbit the Earth and continuously transmit signals |
| GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System) | Russia | Russia’s counterpart to GPS functions similarly with a constellation of satellites transmitting signals to receivers on Earth. Provides global coverage with a focus on northern regions |
| BeiDou | China | China’s satellite navigation system initially started as a regional system but evolved into a global system known as BeiDou-3. It primarily provides coverage in Asia but has expanded to include global coverage, offering capabilities similar to GPS and GLONASS |
| Galileo | European Union | The European Union’s global navigation system aims to provide an independent and reliable satellite navigation system for civilian use. It is still in the process of being fully deployed but is already offering positioning and timing services to users worldwide |
Regional Navigation Systems
Regional Navigation Systems augment GNSS effectiveness within specific areas:
- NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation): India’s system covers the Indian Ocean and neighboring regions, enhancing navigation accuracy and availability.
- QZSS (Quasi-Zenith Satellite System): Japan’s system improves GPS coverage in Asia-Oceania, especially in urban areas and challenging visibility zones.
These regional systems enhance GNSS effectiveness by improving accuracy and availability within their respective areas.
Classification of GNSS
GNSS can be classified into generations based on capabilities:
- GNSS-1 (First Generation): Encompasses GPS and GLONASS, initially developed for military purposes but now utilized for civilian applications globally, augmented by systems like SBAS and GBAS for enhanced accuracy and reliability.
- GNSS-2 (Second Generation): Characterized by fully independent civil satellite navigation systems exemplified by Galileo, offering increased accuracy and availability, incorporating ground-based augmentation systems for improved data accuracy.
Applications of GNSS
The applications of GNSS span various sectors, including military, civilian, and emerging domains:
| Sector | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Military | Navigation | GNSS provides precise positioning and navigation for military forces to operate effectively in various environments |
| Targeting | GNSS helps guide missiles and weapons with high accuracy | |
| Reconnaissance | GNSS supports gathering intelligence by enabling precise location tracking | |
| Civilian | Navigation Systems | GNSS is used in car, airplane, and ship navigation systems for route planning and guidance |
| Surveying & Mapping | GNSS aids in creating accurate maps and measuring land features | |
| Geodesy | GNSS contributes to studying the Earth’s shape and size | |
| Precision Agriculture | GNSS enables farmers to optimize resource use (fertilizers, pesticides) by providing accurate positioning for tractors and equipment | |
| Transportation | GNSS is used for vehicle tracking, fleet management, and logistics optimization | |
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones and wearable devices often incorporate GNSS for location-based services | |
| Emerging | Autonomous Vehicles | GNSS provides precise positioning and navigation crucial for self-driving cars |
| Search & Rescue | GNSS aids in locating lost or stranded individuals | |
| Disaster Management | GNSS helps track disasters and coordinate relief efforts | |
| Asset Tracking | GNSS allows real-time tracking of valuable assets like cargo or equipment | |
| Smart Cities | GNSS contributes to developing intelligent transportation systems, optimizing traffic flow, and managing resources |
References
- “A Beginner’s Guide to GNSS in Europe” (PDF). IFATCA.
- “Galileo General Introduction – Navipedia”. gssc.esa.int.
- “GNSS signal – Navipedia”. gssc.esa.int.
- “IRNSS Programme – ISRO”. www.isro.gov.in.
- Satellite navigation – Wikipedia
- What are Global Navigation Satellite Systems? | NovAtel
- GNSS – Global Navigation Satellite System
- Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and satellite navigation explained