Data Breach
What is a Data Breach?
A data breach is the unauthorized access or disclosure of confidential, protected, or sensitive information. This happens when somebody infiltrates a system, network, or database and uses it for purposes that it was not created for. Data breaches can be very damaging both for people and for organizations, resulting in identity theft, financial loss, reputation damage, and even legal consequences.
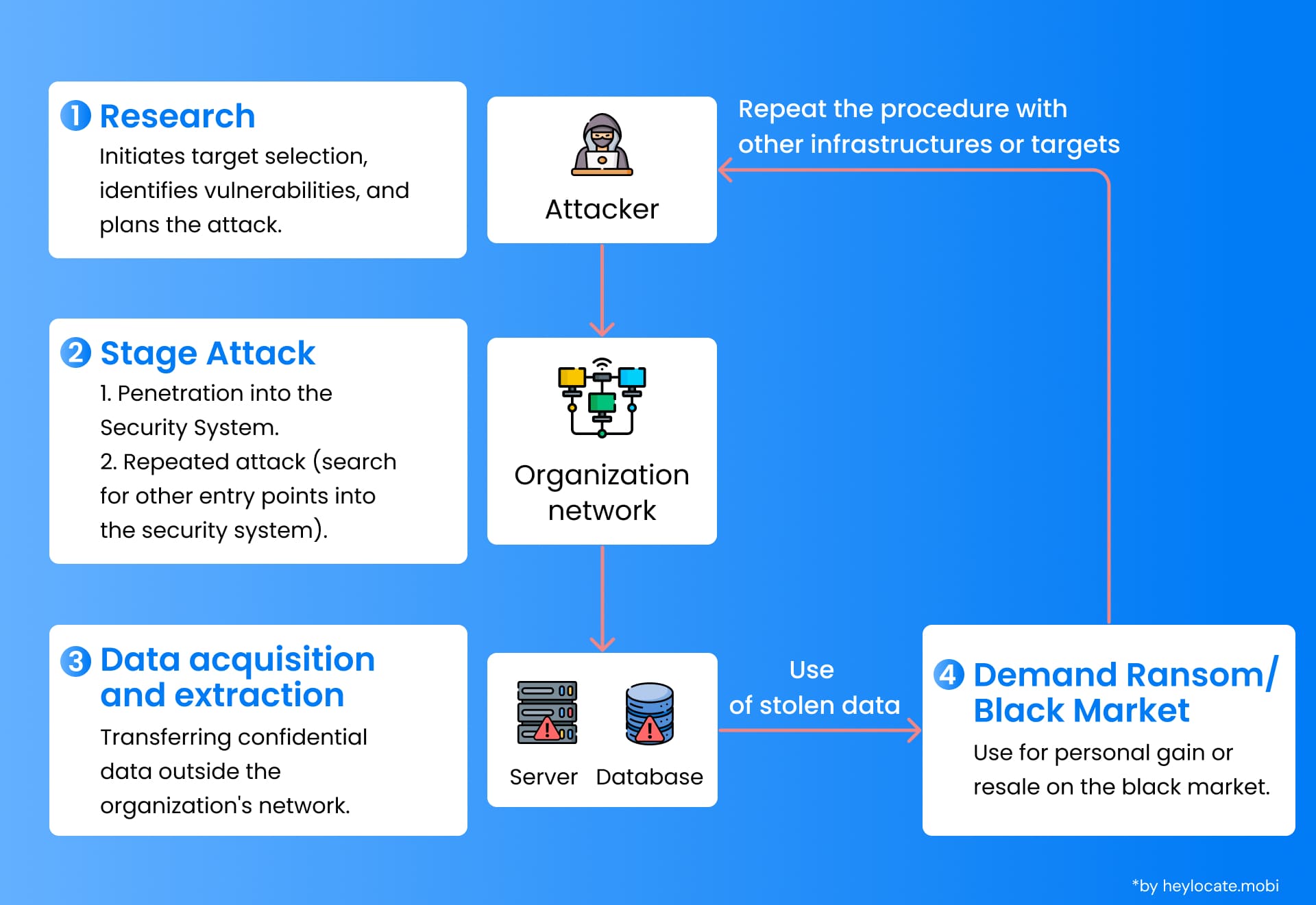
Causes and Types
Multiple variables, both deliberate and accidental, can be the cause of data breaches. One of the main sources is cyber attacks by people or groups whose interest is to use the system’s security loopholes. Such attackers often utilize phishing, malware, or brute force attacks to gain access to confidential information improperly. Security mishaps, such as human errors, software problems or system misconfigurations, are other causes of data breaches. Such incidents, by the way, may unintentionally disclose sensitive data that unauthorized individuals can reach.
There are different types of data breaches, depending on the information that has been compromised. For instance, financial data breaches involve unauthorized access to financial information such as credit card numbers and bank account details. Privacy breaches of personal health data occur when medical records or other health-related information are leaked. On the contrary, corporate information breaches entail the exposure of privileged business data, business secrets or intellectual property.
Consequences of Data Breaches
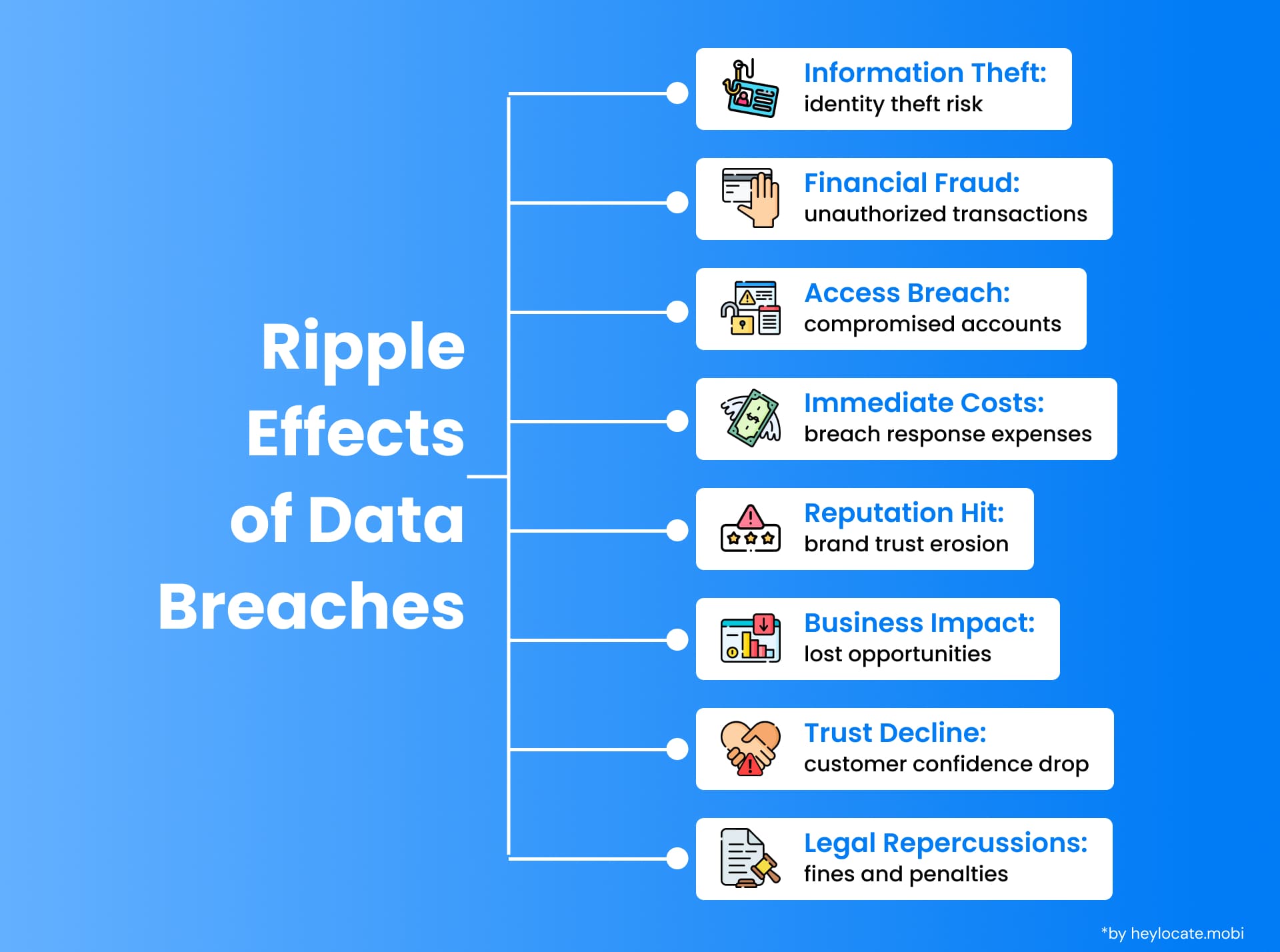
Apart from the immediate impact on individuals and businesses, the implications of a data breach may be wide-ranging and extensive. One of the major concerns is the types of information that can be leaked. Many pieces of sensitive information may be disclosed during a data breach, including bank accounts, personal health records, social security numbers, login credentials, etc. It can result in identity theft, financial fraud, and other cyber-criminals.
Furthermore, one needs to be conscious of the long-term prospects, such as the direct financial and reputational costs. The direct costs include investigating, informing the affected individuals, offering credit monitoring services, and legal charges. Indirect bills include lost business opportunities, damaged brands, and diminished consumer confidence.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Organizations need to be proactive and implement effective strategies to prevent and minimize data breaches. An essential component is the ability to distinguish between insider threats and external threats. Insider threats comprise breaches that happen because of the actions of employees or trusted individuals in an organization, such as intentional data theft or insider trading. On the contrary, the main hazards are attacks by hackers or cybercriminals from outside the organization.
As a solution, organizations can implement strong access controls to prevent insider threats, supervise employee activities and conduct frequent audits of systems and data. Outer threats can be reduced by using strong firewalls, IDS intrusion detection systems, encryption, and periodic security assessments.
The financial impact
Data breaches can cause substantial financial damage to organizations. Direct costs are associated with incident response, forensic investigations, legal fees, and regulatory fines. Indirect costs include business and consumer losses and expenses related to reputation management activities.
The financial impact of data breaches can vary:
- By business sector: for example, in the health care and financial sectors, costs can be higher due to highly sensitive data.
- By countries: due to different regulatory frameworks and legal requirements.
References
- “Leak”. Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press.
- “Chronology of Data Breaches”, Privacy Rights Clearinghouse
- “Information technology — Security techniques — Storage security”. www.iso.org.
- Data breach – Wikipedia
- Data Breach Chronology | Privacy Rights Clearinghouse
- What is a Data Breach? | IBM
- Data Breach – Definition
- How Data Breaches Happen & How to Prevent Data Leaks
- What is a data breach? | Cloudflare