Internet Service Provider (ISP)
What is ISP?
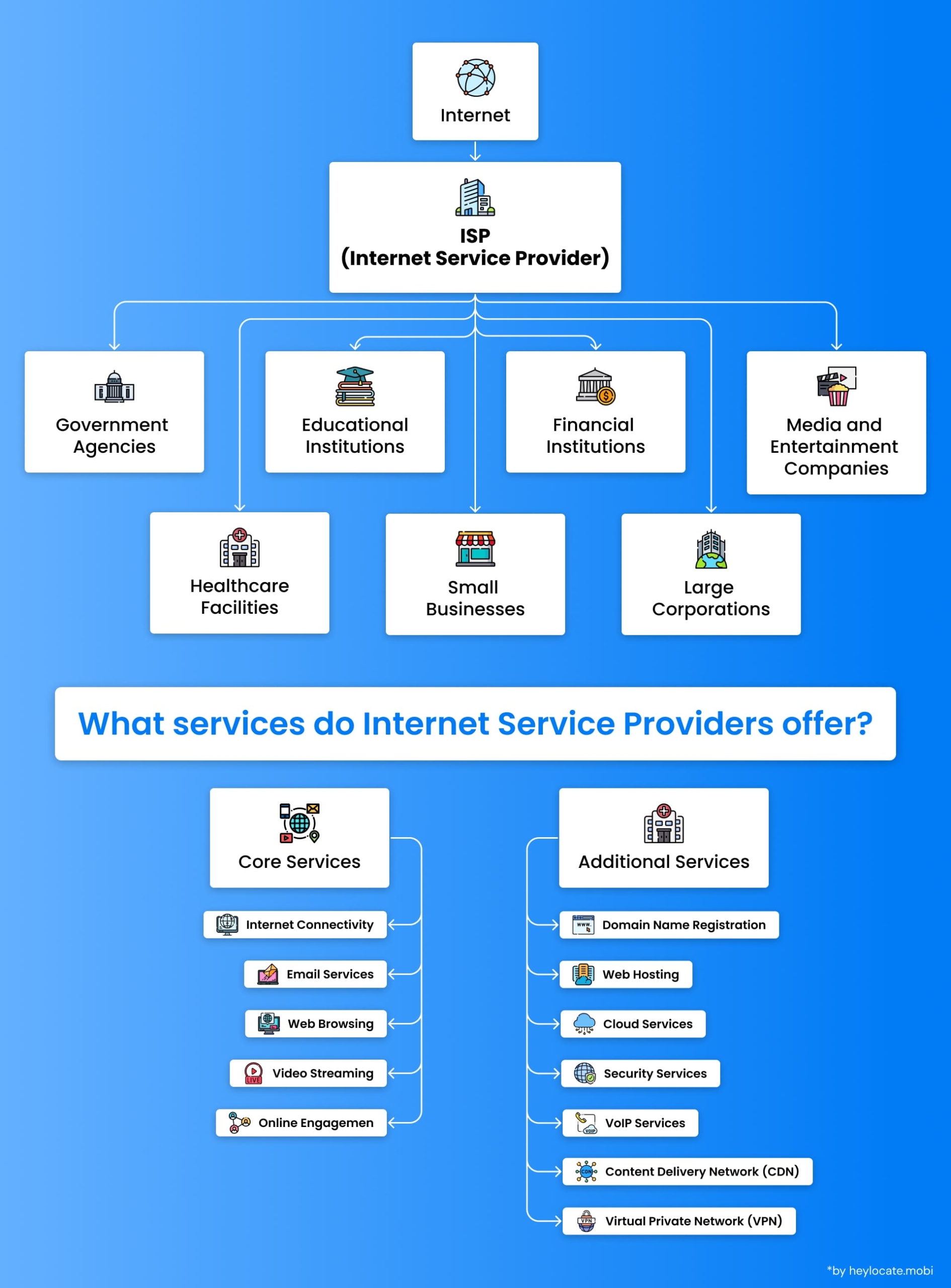
An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is an entity responsible for furnishing Internet access and associated services to individuals, businesses, and organizations. ISPs are crucial in connecting users to the internet, enabling various online activities such as web browsing, email communication, video streaming, and other forms of online engagement. Furthermore, ISPs may extend their services to include additional offerings such as domain name registration, web hosting, and colocation services.
Types of ISPs and Their Services
| Type of ISP | Description | Services Offered |
|---|---|---|
| Access Providers | Most common type of ISP, offering various connection methods | Dial-up, DSL, Cable, Fiber Optics, Satellite |
| Mailbox Providers | Focus on email services | Email hosting, Email servers, Spam filtering, Virus scanning, Email storage |
| Hosting ISPs | Specializing in web hosting services | Server space, Web hosting, Domain name registration, Website builders, Content management systems |
| Transit ISPs | Providing connectivity between different networks and ISPs | Intermediary services, High-speed backbone networks |
| Virtual ISPs (VISPs) | Lease network capacity from other ISPs to provide internet access | Niche or regional focus, Competitive pricing, Specialized services |
| Free ISPs | Provide internet access at no cost | Advertising-based, Premium service offerings |
| Wireless ISPs (WISPs) | Utilize wireless technology for internet access | Radio waves, Microwave transmissions, Mobile networks, On-the-go connectivity |
References
- Internet service provider – Wikipedia
- What is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)? Definition & Meaning Explained
- Internet Service Provider (ISP): What They Do and Examples
- What Is an ISP? Everything You Need to Know
- What is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
- What is an ISP? — Definition and responsibilities
- What Is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?