Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
What is a URL?
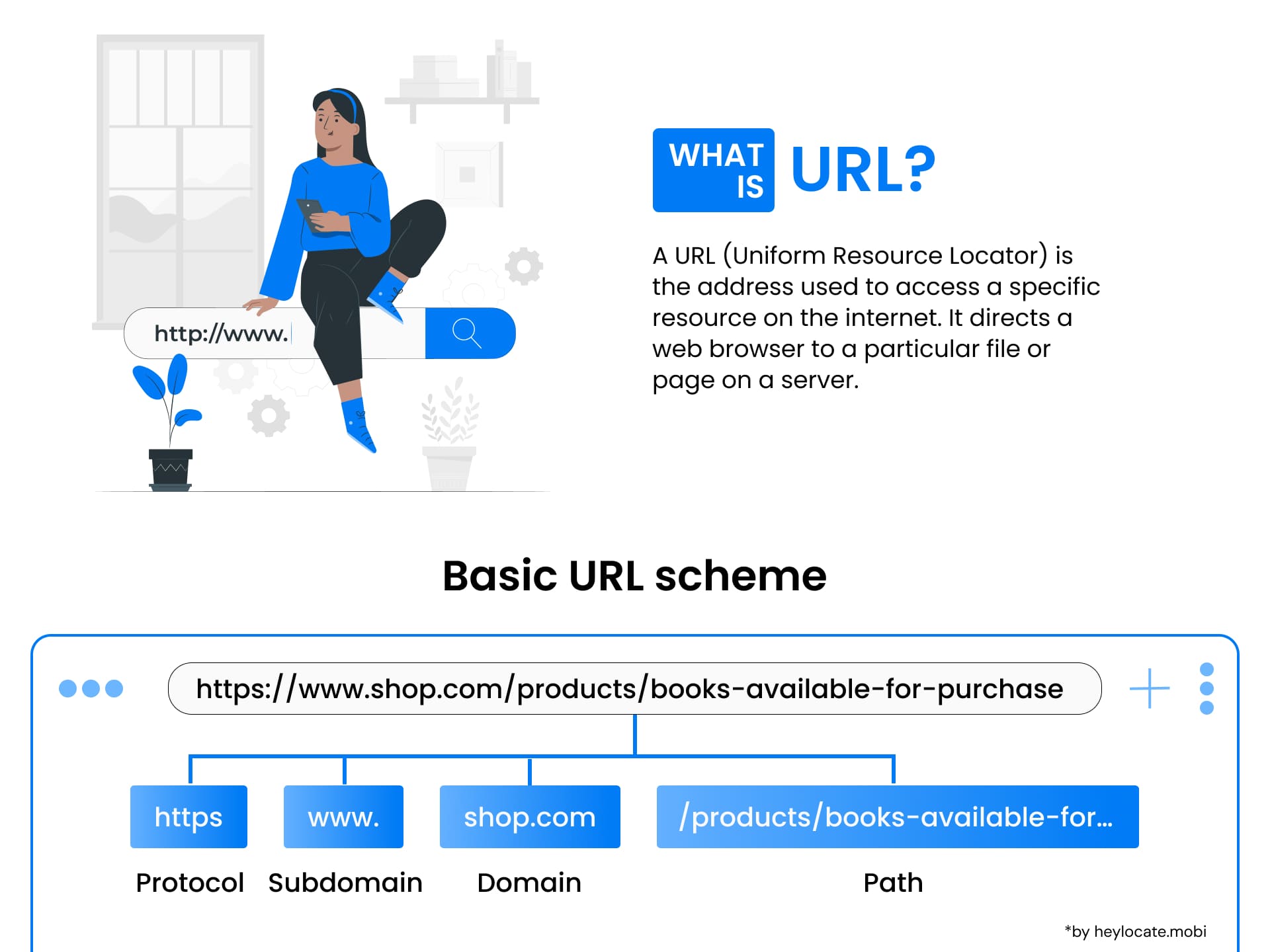
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is a reference (an address) to a resource on the Internet. It is fundamental for identifying and locating resources on the web, allowing users to access specific web pages, documents, or any other digital resource available on the internet. URLs are a subset of Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs), specifically denoting the means by which a resource can be accessed.
Applications and Uses
URLs have various applications beyond web browsing:
- File Transfer: URLs are used in File Transfer Protocols (FTP) to download or upload files from servers.
- Email: URLs enable clickable links within email messages.
- Database Access: URLs facilitate accessing databases for querying and retrieving information.
Structure of a URL
A URL consists of several components that work together to pinpoint a specific resource:
- Scheme: Indicates the protocol used to access the resource (e.g., “http://”, “https://”).
- Authority: Specifies the server hosting the resource, including the domain name or IP address and optionally a userinfo subcomponent for authentication.
- Path: Identifies the specific location of the resource on the server, typically represented by directories and filenames.
- Query: Allows for additional parameters to be passed to the server (e.g., for search queries or filtering).
- Fragment: Points to a specific section within a resource, often used with anchor tags or bookmarks.
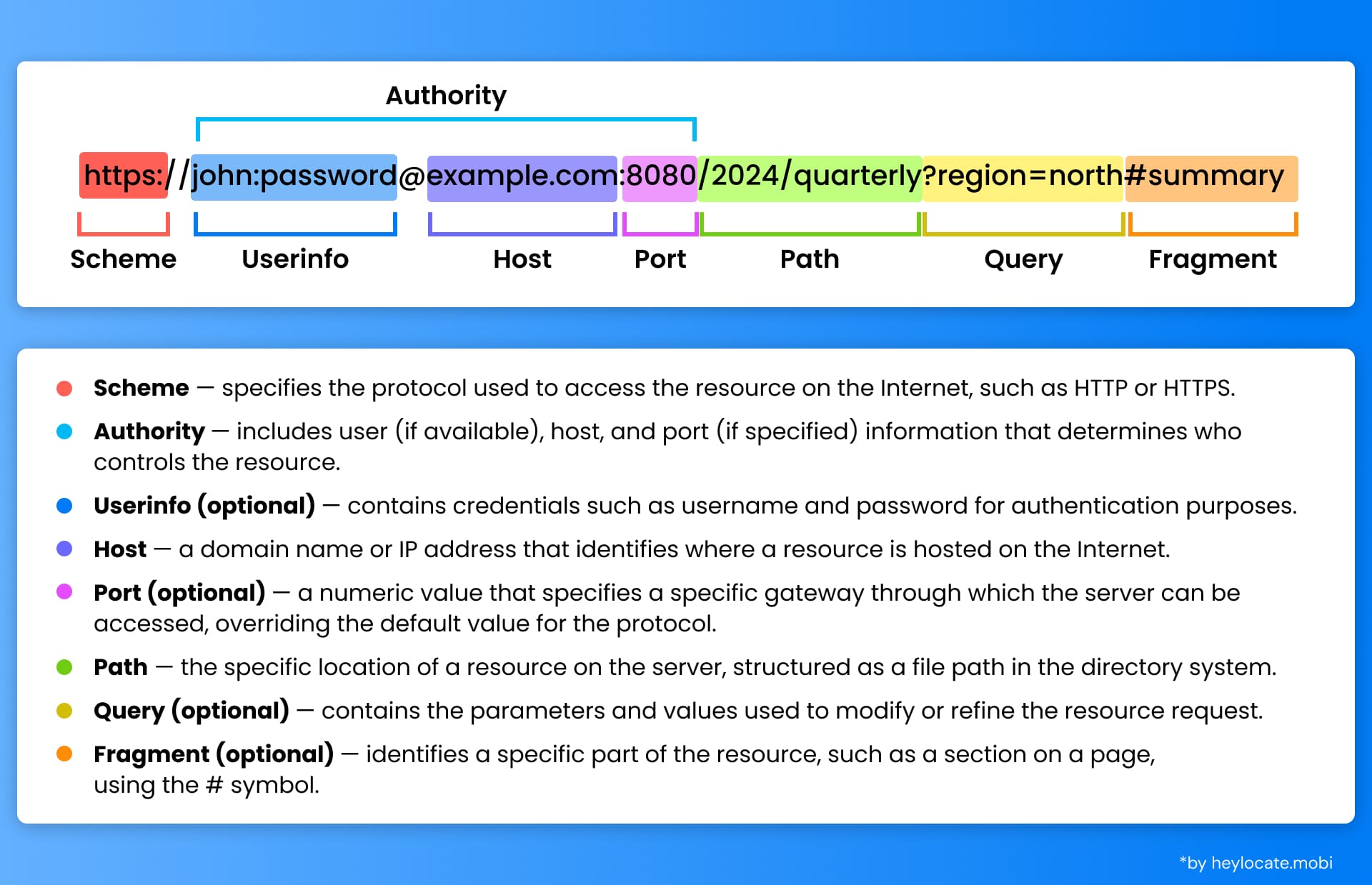
Authority Component Analysis
The authority component of a URL plays a crucial role in identifying the server hosting the desired resource. It consists of subcomponents such as userinfo, host, and port. The host subcomponent represents the domain name or IP address of the server, serving as the primary identifier for the server hosting the resource.
The port subcomponent may be included to specify a specific port number to connect to on the server. If no port is specified, the default port for the given scheme is used.
Path, Query, and Fragment Components
The path component of a URL identifies the specific location of the resource on the server, often represented by a series of directories and filenames.
The query component allows for additional parameters to be passed to the server, typically in the form of key-value pairs. The fragment component specifies a specific section within the resource, often identified by an anchor tag or bookmark.
References
- URL – Wikipedia
- Uniform Resource Identifier – Wikipedia
- What is a URL? – Learn web development | MDN
- What is a URL (Uniform Resource Locator)? Definition from SearchNetworking
- What Is a URL? A Complete Guide to Website URLs
- What Is A URL? Find Out What A URL Stands For and Its Meaning – Verisign
- Internet Basics: Understanding URLs