Wide Area Network (WAN)
What is WAN?
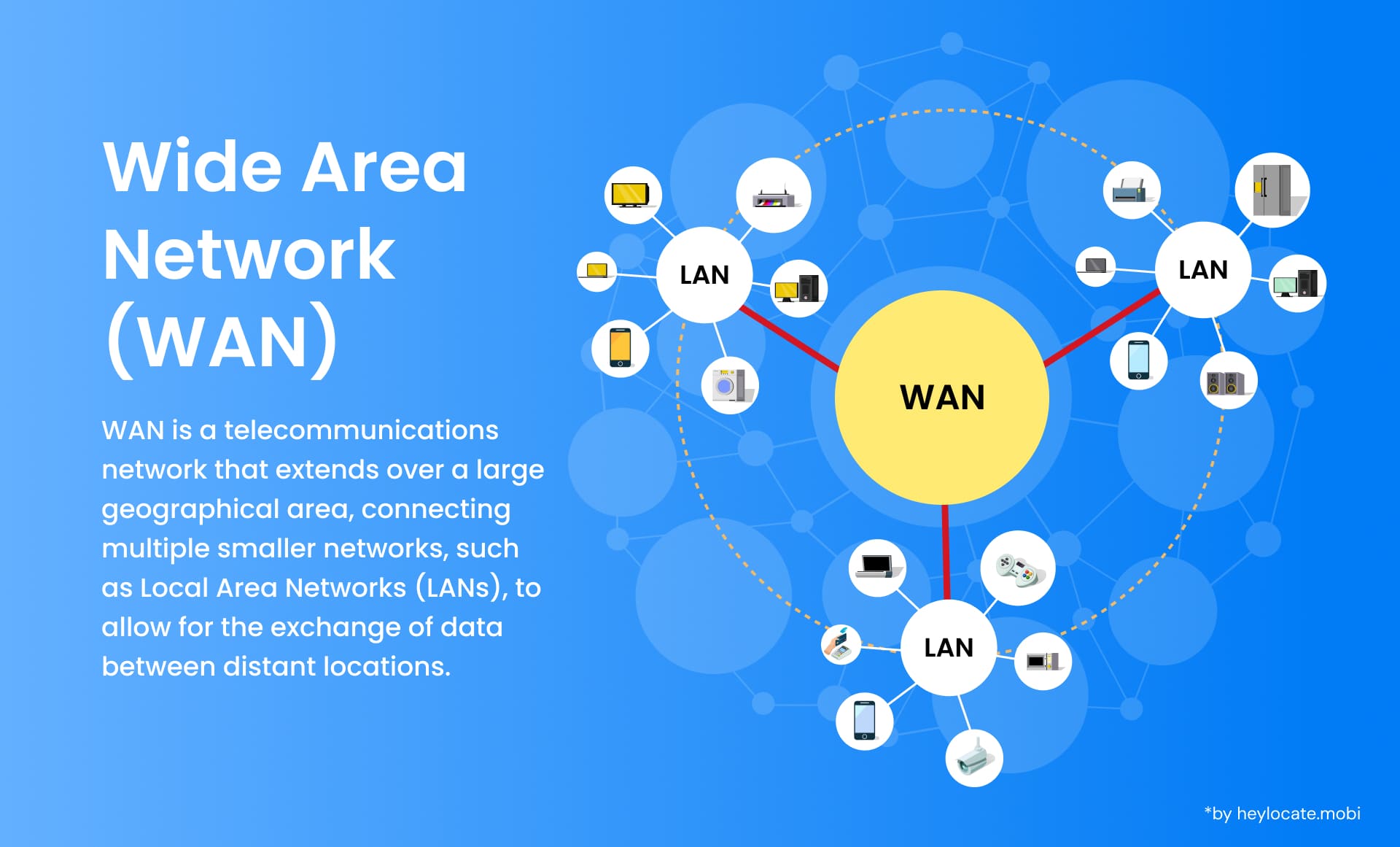
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a telecommunications infrastructure traverses extensive geographical distances. It serves to interconnect Local Area Networks (LANs) and other networks, facilitating communication and resource sharing among devices situated in various locales. WANs are indispensable for enterprises, academic institutions, and government organizations seeking to function across dispersed geographical regions or even continents.
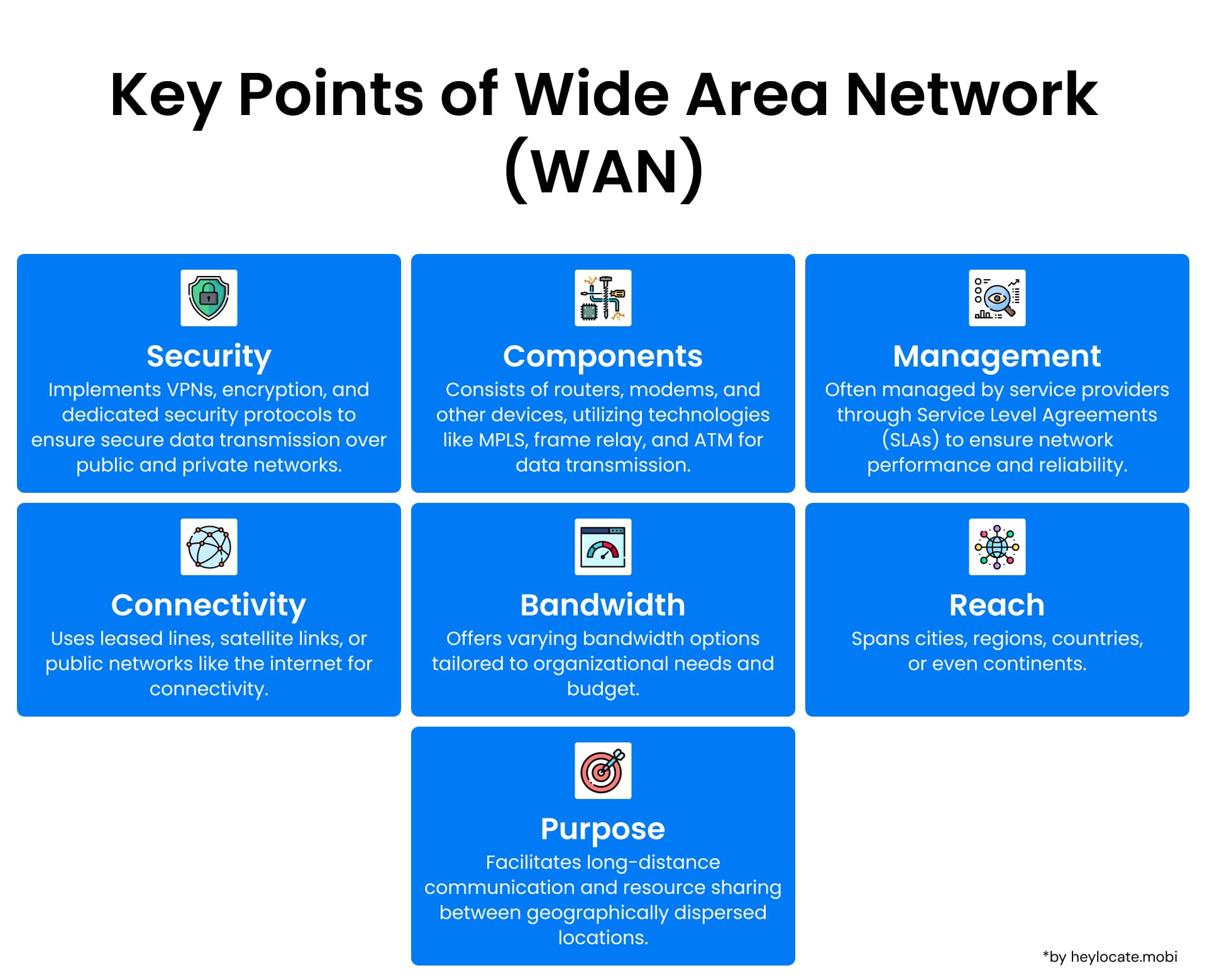
Design Options
- Network Span and Applications: The geographical scope of WANs can range from regional networks to those spanning entire nations or the globe. Designing an effective WAN hinges on the specific requirements of the organization employing it. A primary role of WANs involves linking multiple LANs and extending network reach beyond a single locale.
- Communication Protocols: Successful WAN design necessitates the utilization of various communication protocols to ensure dependable and efficient data transmission. A cornerstone protocol suite used in WANs is the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which guarantees data integrity and seamless communication between disparate networks.
Innovations and Future Directions
Recent years have witnessed groundbreaking advancements in WAN technology, promising even swifter and more reliable communication. A case in point is the introduction of 400-gigabit Ethernet, which has revolutionized network speeds, enabling data transfer at unparalleled rates.
Research Areas in WAN
Academic research helps in advancing the field of Wide Area Networks, their design, performance, and security. Three principal research areas include:
- Mathematical models provide a theoretical framework for analyzing and optimizing WAN performance.
- Network emulation concentrates on creating authentic replicas of Wide Area Network (WAN) environments, serving as testing grounds for innovative technologies and protocols.
- Network simulation are used to scrutinize and anticipate the behavior of WANs under a myriad of conditions.
WAN Optimization
WAN optimization incorporates diverse technologies and methodologies designed to augment data transmission efficiency and diminish network latency. Wide Area File Services (WAFS) is a cornerstone technology in this field, which facilitates centralized storage and expedites access to files across a WAN. This strategy negates the requirement for local file servers at each site, simplifying data management and overall network performance. By directing attention to these optimization tactics, organizations can guarantee that their WANs remain adaptable, efficient, and adept at addressing the dynamic needs of contemporary communication.
References
- Wide area network – Wikipedia
- What is WAN? – Wide Area Network Explained – AWS
- What Is a WAN? Wide-Area Network – Cisco
- What is WAN | Wide Area Network Definition | Computer Networks | CompTIA
- What Is a Wide Area Network (WAN)? Definition, Types, Architecture, and Best Practices – Spiceworks
- What is WAN? – Techtarget
- What is WAN? Wide-Area-Network Defined | Fortinet