Local Area Network (LAN)
What is LAN?
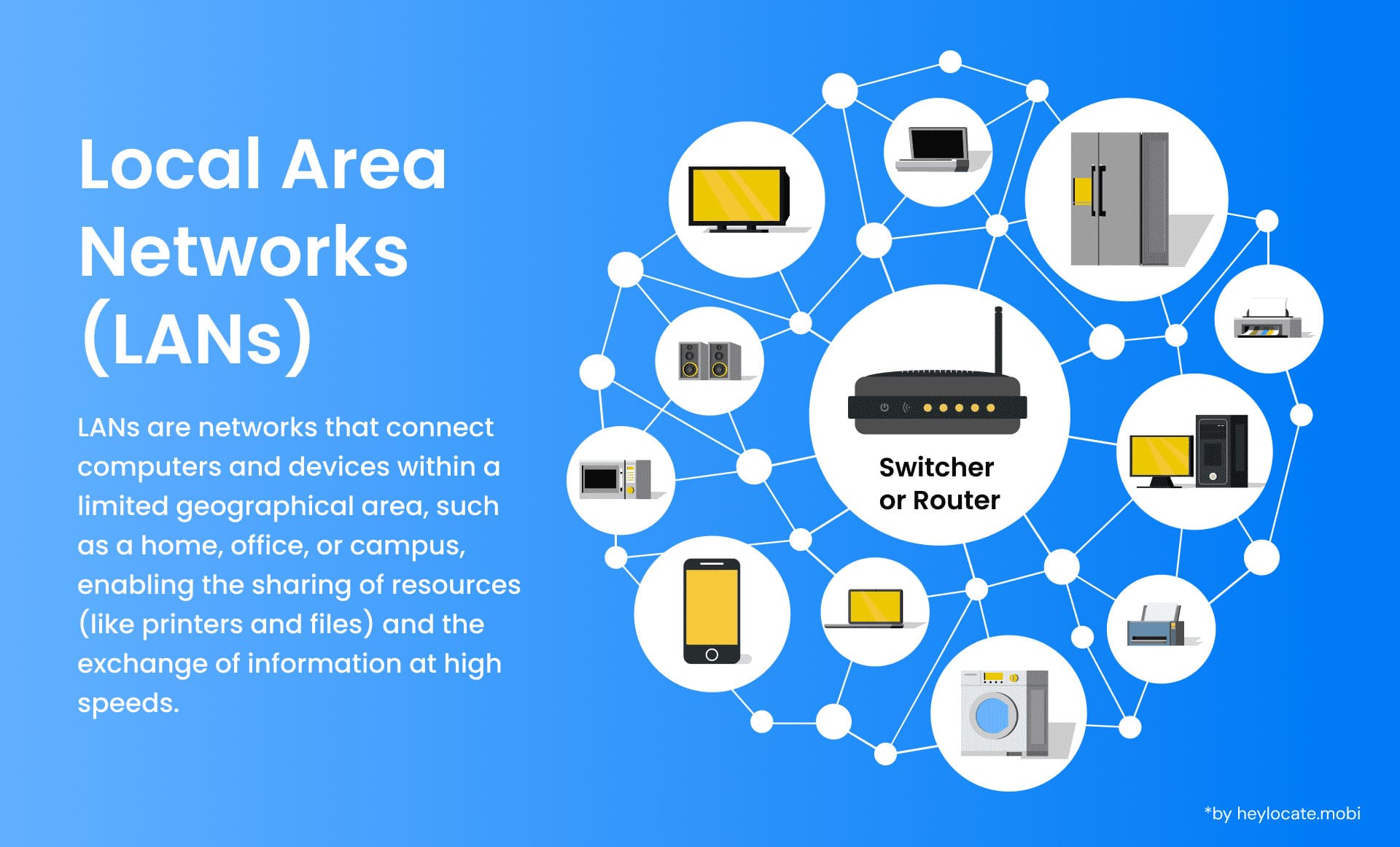
A local area network (LAN) is a term used in computer networking to refer to a network that connects devices within a limited geographical location, such as an office building, school, or house. The main aim of LAN is to enable communication and sharing of resources among the connected devices in the network. Through setting up a LAN, users can efficiently transfer files, printers, and other network devices, which enhances collaboration and productivity.
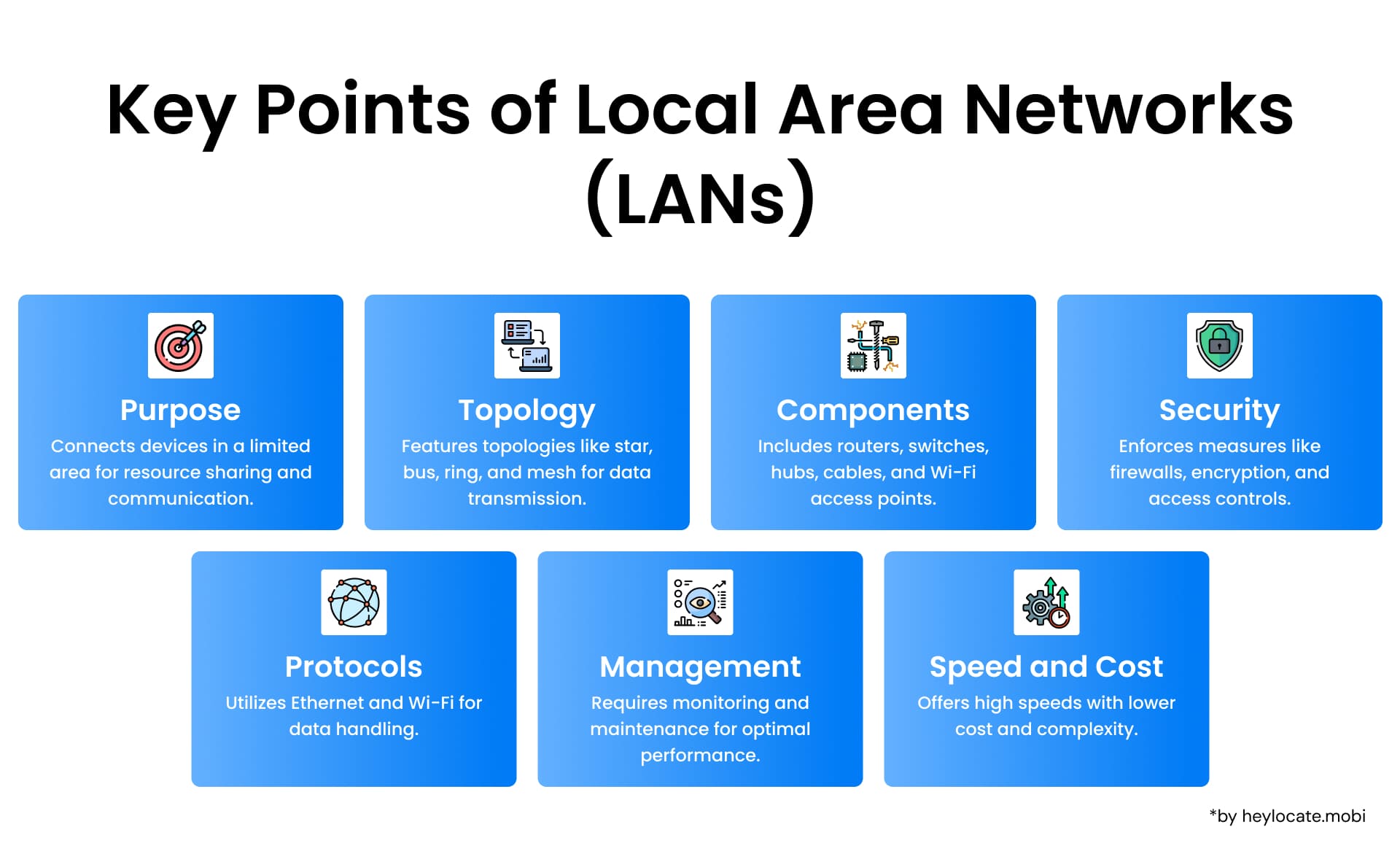
LAN Components and Connectivity
A LAN has multiple computers, servers, printers, and other devices connected over wired or wireless connections. These devices are interrelated using switches, routers, and access points to enable the passing of data packets from one device to another. In a LAN, devices can communicate with each other directly without involving data passing through the external networks.
LAN vs. WAN
| Feature | Local Area Network (LAN) | Wide Area Network (WAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Coverage | Limited to a small area, such as a building, campus, or complex | Spans a large area, connecting LANs and other networks across cities, regions, or even globally |
| Network Topology | Typically simple, using star or bus topology | Complex, often involving multiple routers, switches, and other network devices |
| Ownership | Privately owned and managed by a single organization or individual | Owned and managed by multiple organizations, service providers, or telecommunication companies |
| Data Transfer Speed | High-speed connections, usually ranging from 10 Mbps to 100 Gbps | Lower data transfer speeds compared to LANs, typically ranging from 1.5 Mbps (T1 line) to several Gbps, depending on the service provider and technology used |
| Latency | Low latency due to short distances between connected devices | Higher latency compared to LANs, caused by longer distances and potential data routing through multiple networks |
| Security | Generally more secure due to a smaller network footprint and direct control over network components | More vulnerable to security threats due to the involvement of third-party service providers and potential exposure to public networks |
Core Technologies Behind LAN
Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two primary technologies used for LAN connectivity.
- Ethernet: Developed in the 1970s, it’s the de facto standard for wired LANs. It uses CSMA/CD to manage network access. Ethernet cables connect devices to switches.
- Wi-Fi: Provides wireless LAN connectivity. It uses radio waves and adheres to the IEEE 802.11 standard, enabling mobility and flexibility.
LAN Development Timeline
Early Days
- LANs focused on sharing expensive resources, maximizing resource utilization, and centralizing resources for multiple users.
As PCs Became Prevalent
- LANs were used for networking individual PCs, enabling file sharing, collaboration, and effective communication.
1980s
- Novell NetWare emerged, providing a standardized platform for LAN implementation.
Rapid Proliferation of LAN Technologies
- Development of networking standards, such as IEEE 802.3 for Ethernet, ensured compatibility and facilitated widespread adoption.
1990s
- Novell NetWare and Banyan Vines offered robust features for file and print sharing, user authentication, and network management.
- 3Com 3+Share aimed to provide an affordable LAN solution for small businesses.
Adoption of TCP/IP
- TCP/IP replaced proprietary protocols, enabling seamless integration of LANs with the internet.
Present
- LANs built on Ethernet or Wi-Fi, relying on TCP/IP for communication.
- Convergence of technologies has revolutionized the way we connect and communicate.
- LANs are an essential component of modern computing infrastructure.
References
- Local area network – Wikipedia
- What is a LAN? Local Area Network – Cisco
- What is a LAN (local area network)? | Cloudflare
- What Is Local Area Network (LAN)? Definition, Types, Architecture, and Best Practices – Spiceworks
- LAN Definition | What Is Local Area Network | Computer Networks | CompTIA
- What is a LAN (local area network)? Neosnetworks
- Local area network (LAN) | Britannica