GPS Spoofing
What is GPS Spoofing?
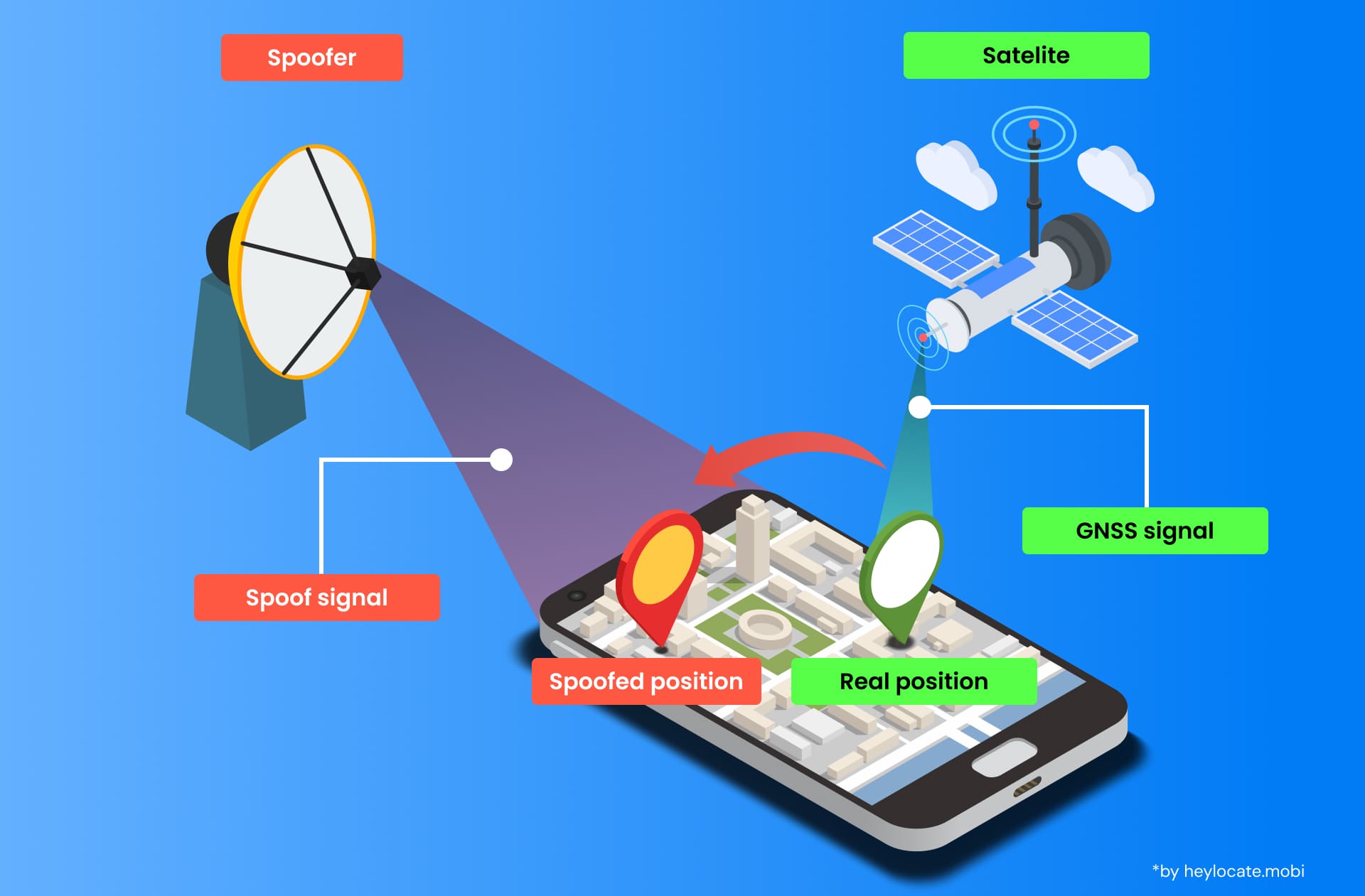
GPS spoofing is the intentional manipulation of signals from the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) to deceive receivers into providing inaccurate location or time data. This manipulation is achieved by broadcasting false signals that mimic those transmitted by genuine satellites.
Mechanisms of GPS Spoofing
The mechanisms employed in GPS spoofing vary, but they often entail transmitting counterfeit signals that overpower legitimate signals received by the receiver. One common method is the carry-off attack, wherein the attacker sets up a high-powered transmitter near the target receiver and broadcasts fake signals stronger than GPS satellites. Consequently, the receiver, unable to differentiate between real and fake signals, locks onto the spoofed signals and outputs inaccurate positioning information.
Strategies to Combat GPS Spoofing
To mitigate the threat of GPS spoofing, several strategies can be employed:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Deterrence | Techniques like antenna obscuration make it harder for attackers to target receivers. This can involve shielding antennas or placing them in less accessible locations |
| Multi-GNSS Reception | Utilizing signals from multiple GNSS constellations (GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou) can help identify discrepancies caused by spoofing. Inconsistencies between navigation systems might indicate an attack |
| Advanced Detection Techniques | Analyze data from various vehicle sensors (e.g., speedometers, accelerometers) to compare expected motion with GPS information. Discrepancies can potentially reveal spoofing |
| Cooperative Communication Systems | Leverage communication between vehicles (e.g., CACC) to detect inconsistencies in relative positioning data, potentially revealing spoofing attacks on autonomous vehicles |
| Ongoing Research and Development | Continuous efforts are crucial to stay ahead of attackers. This might involve exploring new anti-spoofing technologies and improving existing detection methods |
References
- Coffed, Jeff (February 2014). “The Threat of GPS Jamming The Risk to an Information Utility” (PDF). Exelis.
- Jon S. Warner; Roger G. Johnston (December 2003). “GPS Spoofing Countermeasures”. homelandsecurity.org.
- What Is GPS Spoofing and How Do You Defend Against It? | Okta
- Spoofing attack – Wikipedia
- What is GPS spoofing? | McAfee
- GPS Spoofing – DataVisor Digital Fraud Wiki
- GPS Spoofing