GPS Tracker
What is a GPS Tracker?
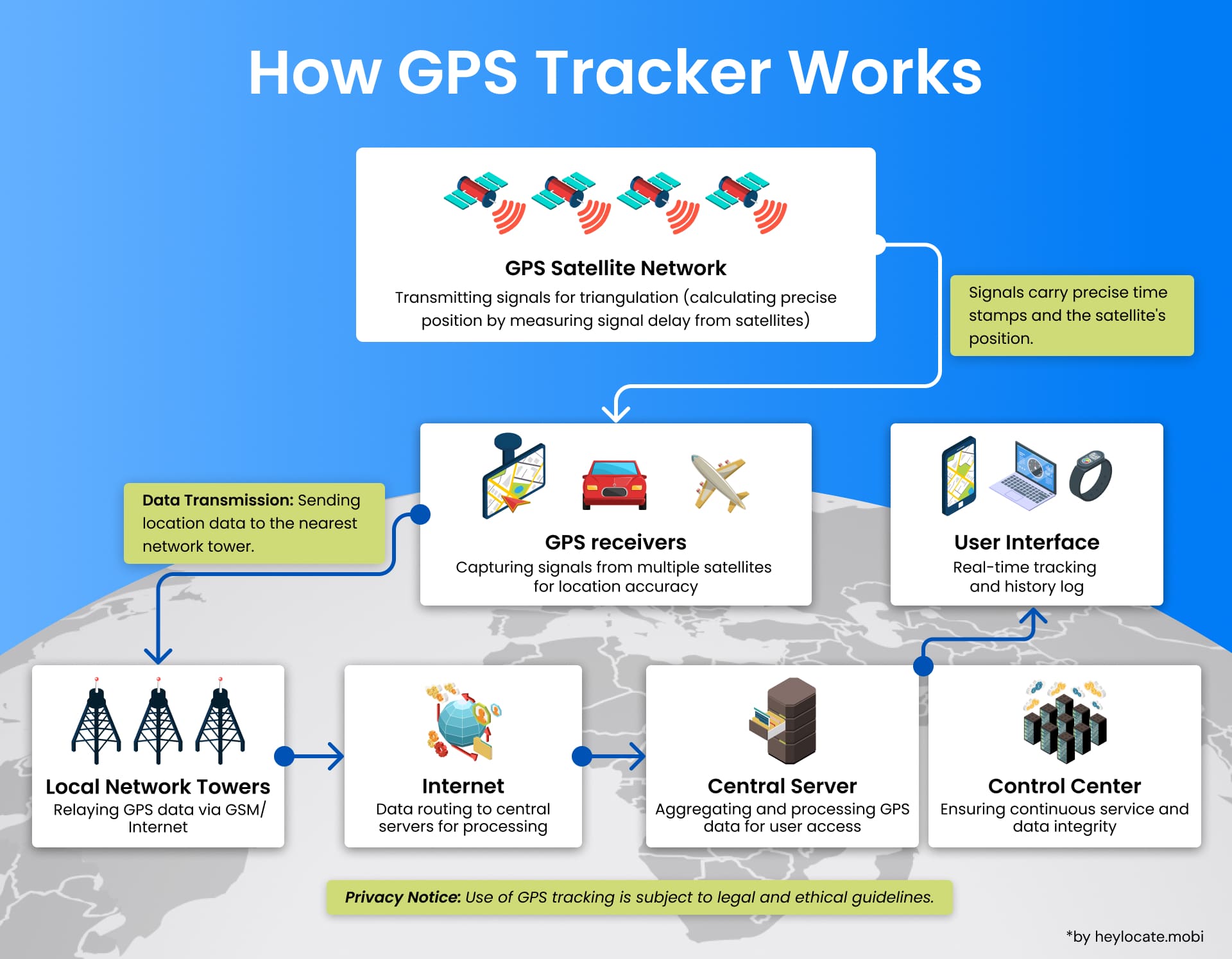
A GPS tracker is a device leveraging the Global Positioning System (GPS) to pinpoint the exact location of an object or individual. It operates by receiving signals from a network of orbiting satellites, which are then utilized to calculate the precise coordinates. This data is subsequently transmitted to a central server or user interface for visualization and analysis.
Components and Functionality
Understanding the operational mechanics of GPS trackers necessitates an examination of their fundamental components, tracking and communication technologies, and the software facilitating data visualization and analysis.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| GPS Module | Receives signals from GPS satellites to compute precise coordinates |
| Data Logger Memory | Stores location data for future retrieval and analysis |
| Communication Modem | Transmits location data to a central server or user interface |
Tracking and Communication Technologies
The software associated with GPS tracking enables users to establish Geofence — virtual boundaries, triggering alerts upon entry or exit by a tracker. This functionality proves valuable in scenarios such as child monitoring or asset protection. Moreover, the software facilitates the generation of comprehensive reports and analytics based on tracking data, furnishing valuable insights for decision-making and optimization.
Types of GPS Trackers
GPS trackers are available in diverse types tailored to specific tracking requirements:
- Data Loggers: Ideal for wildlife monitoring and storing location data for subsequent analysis.
- Data Pushers: Suitable for vehicle tracking and personal safety, transmitting real-time location data.
- Data Pullers: Permit on-demand access to location data, which is conducive to periodic tracking or battery conservation.
- Covert GPS Trackers: Designed for discreet tracking in surveillance or monitoring endeavors.
Applications of GPS Trackers
GPS trackers find utility across various industries and sectors with common applications. These are the common ways that GPS trackers are used.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Tracking and Safety | Monitor the location of loved ones (children, elderly) or for personal safety in outdoor activities | Peace of mind improves safety and allows for emergency response | Privacy concerns, the potential for misuse |
| Vehicle and Asset Tracking | Track the location and movement of vehicles (fleet management) or valuable assets (equipment, containers) | Optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, improve efficiency, and enable theft recovery | Cost of implementation, data security |
| Commercial and Business Use | Track the location of delivery vehicles and monitor employee movement (field workers) | Improve delivery efficiency, ensure employee accountability, and optimize resource allocation | Employee privacy concerns the potential for misuse |
| Animal and Wildlife Monitoring | Study animal behavior, migration patterns, and habitat usage | Gain valuable data on wildlife, improve conservation efforts, and track endangered species | Potential impact on animal behavior, ethical considerations |
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Deploying GPS trackers necessitates adherence to legal and ethical frameworks, encompassing:
- Privacy and Surveillance Laws: Compliance with jurisdictional regulations concerning GPS tracker usage, including consent and notification requirements.
- Consent and Ownership Issues: Obtaining explicit consent and informing individuals about tracking activities to respect privacy rights and ownership considerations.
- Impact on Personal Freedoms: Balancing the benefits of GPS tracking with the protection of personal freedoms and privacy rights, ensuring responsible usage and respect for individual autonomy.
References
- “WGS84”. wiki-georef.
- “GPS Cycle Computer v3”. Axivo Inc.
- “Free Eriadne.org tracking system”.
- GPS tracking unit – Wikipedia
- Commercial GPS Tracking System: What is it and How Does it Work? – MiX Telematics
- Introduction to GPS tracking: A brief overview of what GPS tracking is and how it works
- How a GPS Tracker Works – Trackimo