Latitude
What is latitude?
Latitude is a core geographical concept determining the north-south positions on Earth and other celestial bodies. It is the angular distance from the Equator, and when put together with latitude, it creates a coordinate system that enables the precise location of any point on the Earth’s surface.
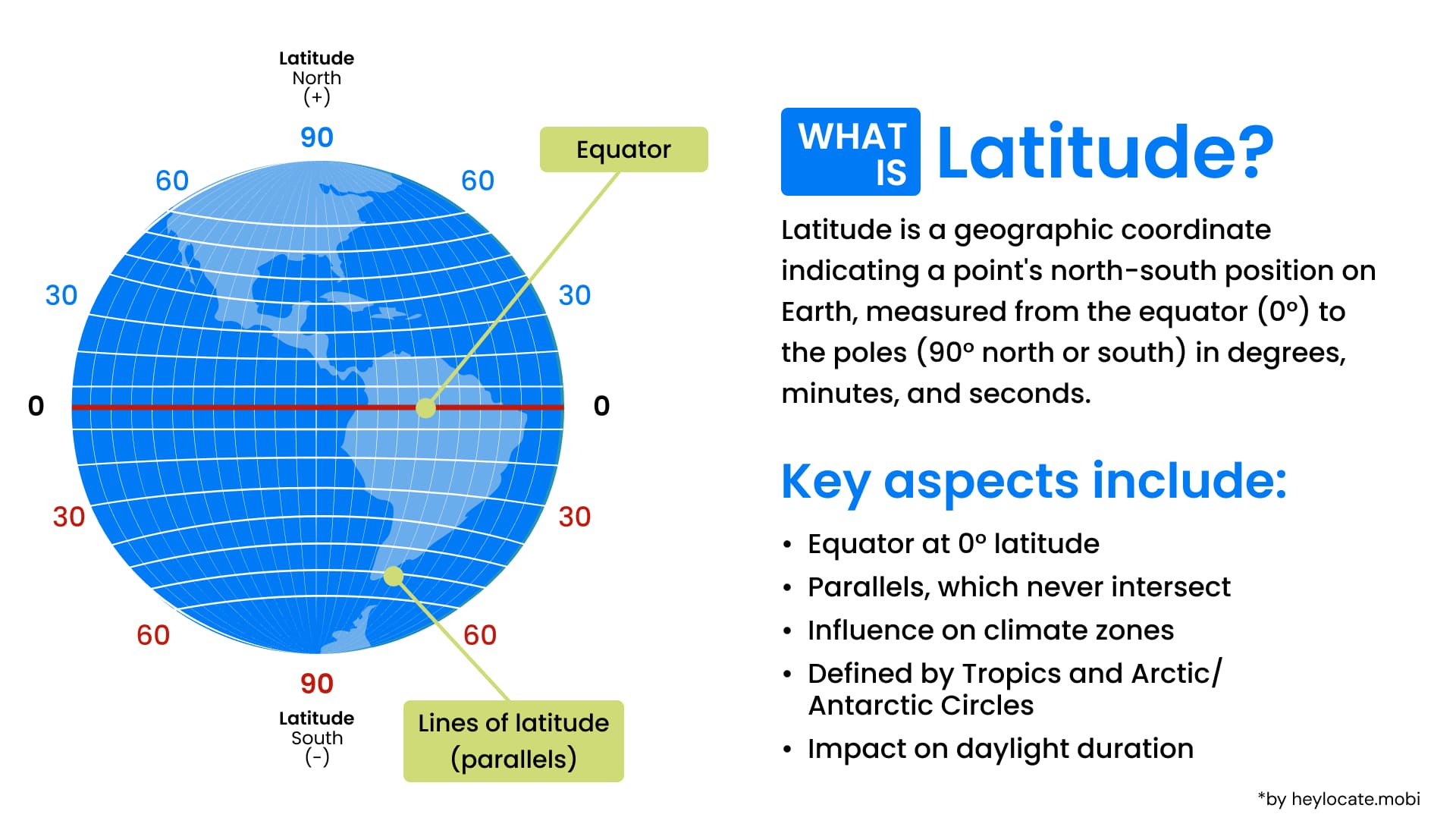
Understanding Latitude
Latitude is an angle ranging from -90º to +90º, signifying the position north or south of the Equator.
This angular measurement divides the earth into fantasy lines called parallels. They run parallel to the Equator and form a part of the system called the graticule, used in cartography and navigation.
Geodetic latitude is a type of latitude that preserves the Earth’s irregular shape, providing a more accurate indication of the location’s position.
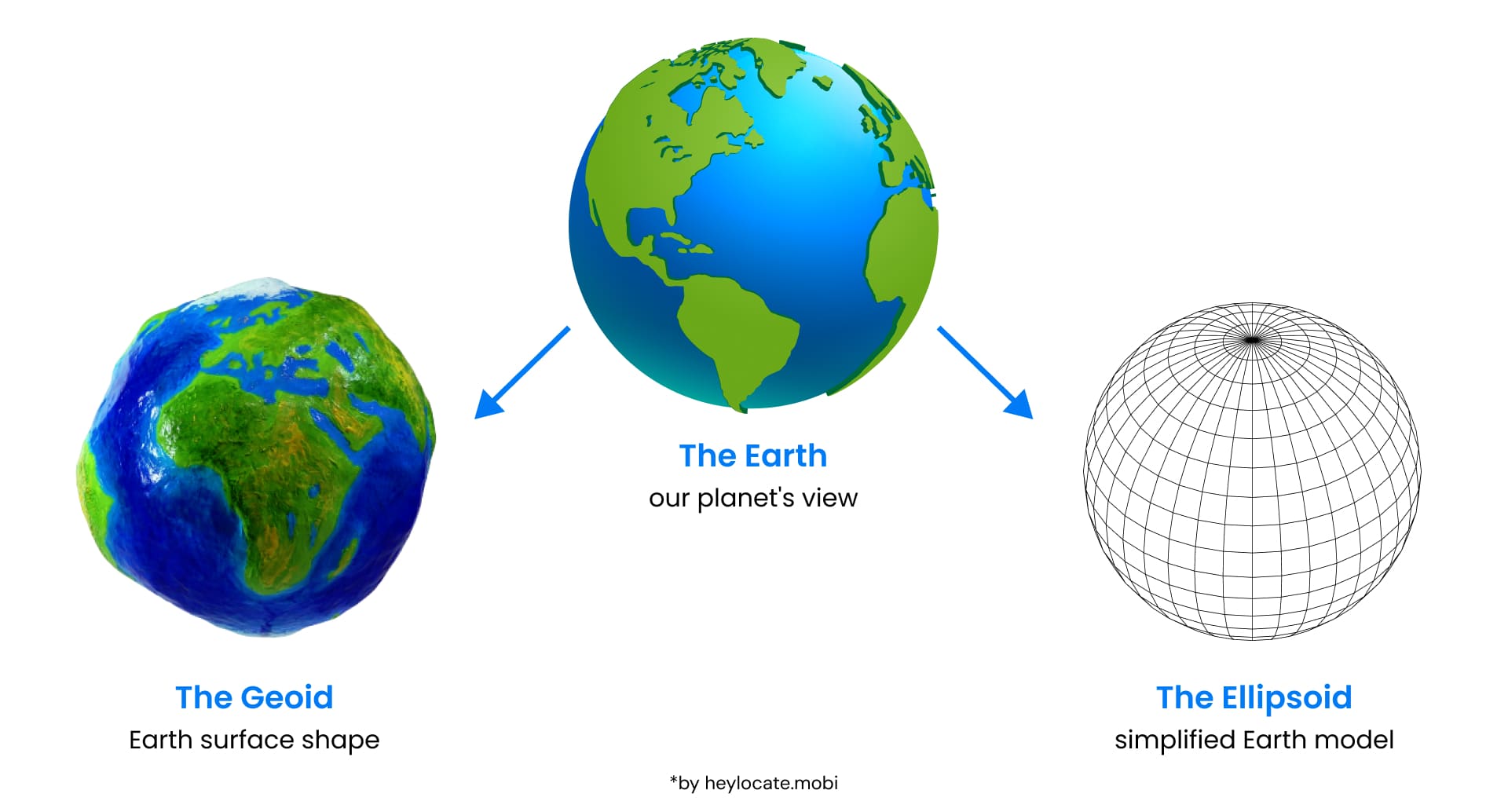
Geoid and Reference Surfaces
The geoid portrays the shape of the earth’s surface, including the irregularities caused by gravity and mass distribution.
The geoid is usually simplified by using reference surfaces such as ellipsoids of revolution.
An ellipsoid of revolution is a mathematical approximation of Earth’s spherical shape. It is formed by the rotation of an ellipse around its minor or major axis, producing two kinds: oblate and prolate ellipsoid.
Technical Aspects of Latitude
| Latitude Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Latitude on the Sphere | Visualization of latitude on a spherical model of the Earth | Equator (0°), Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N), Arctic Circle (66.5° N) |
| Latitude on the Ellipsoid | Latitude taking into account the Earth’s actual shape as an ellipsoid | Geodetic latitude, different reference ellipsoids (e.g., WGS84) |
Advanced Concepts in Latitude
| Auxiliary Latitude | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Geocentric Latitude | The angle between a line from the Earth’s center to a point on the surface and the equatorial plane | Satellite orbits and space-based applications |
| Parametric Latitude (Redfearn Latitude) | Latitude used in the construction of certain map projections, e.g., Transverse Mercator | Map projections and coordinate transformations |
| Rectifying Latitude | The latitude at which the meridian has the same scale as the equator on a map projection | Equal-area map projections |
| Authalic Latitude | Latitude used in the creation of authalic (equal-area) map projections | Equal-area map projections |
| Conformal Latitude | Latitude used in the creation of conformal (angle-preserving) map projections | Conformal map projections |
| Isometric Latitude | Latitude is used in the creation of map projections that preserve distances along meridians and parallels | Map projections with specific distance-preserving properties |
Practical Applications of Latitude
| Application Area | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Navigation | Latitude is essential for determining positions and planning routes on land and at sea | Maritime and aviation navigation, hiking, orienteering |
| Mapping and Coordinate Systems | Latitude is a fundamental component of various mapping and coordinate systems | Geographic coordinate system, map projections, GIS |
| Astronomy | Latitude is used to determine the position of celestial objects relative to the Earth’s equator | Celestial navigation, astronomical observations |
| Modern Technology | Latitude is utilized in modern technology for precise location information | Global Positioning System (GPS), satellite tracking, location-based services |
References
- Latitude – Wikipedia
- What is latitude? Noaa.gov
- Latitude. National Geographic
- Latitude Definition & Examples – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
- What is Latitude? Glossary
- What is longitude? | Royal Museums Greenwich
- Latitude and longitude | Definition, Examples, Diagrams, & Facts | Britannica