Keylogger
What is Keylogger?
A keylogger is a software or hardware that records keystrokes executed on a computer or mobile device. Commonly referred to as keystroke loggers, these tools are crafted to meticulously capture every keystroke made, encompassing sensitive data such as passwords, usernames, and other confidential information. Keyloggers serve diverse purposes, ranging from employee activity monitoring and parental control to research initiatives.

Types and Methods of Keylogging
Primarily there are two types of keylogging:
- Software-based
- Hardware-based
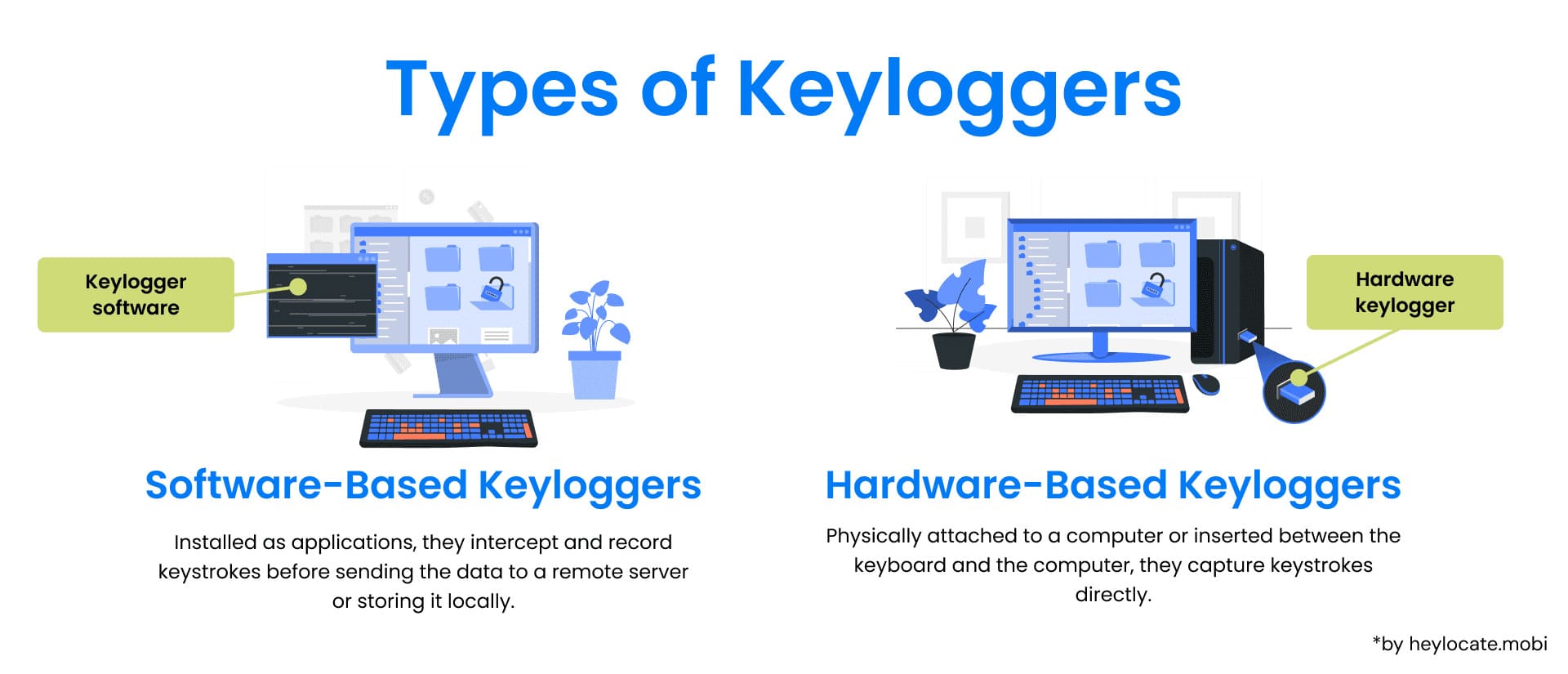
Tables comparing two types of Keylogging:
| Category | Type | Description | Difficulty to Detect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software-Based | Hypervisor-based | Operates at a very low level, capturing keystrokes before encryption | High |
| Kernel-based | Intercepts keystrokes at the operating system kernel level | Medium | |
| API-based | Captures keystrokes from specific applications using application programming interfaces | Medium | |
| Form grabbing-based | Steals data entered into web forms | Medium | |
| JavaScript-based | Runs in web pages to capture keystrokes within the browser | Low (can be blocked by security software) | |
| Memory-injection-based | Injects malicious code into running processes to capture keystrokes | Medium to High |
| Category | Type | Description | Difficulty to Detect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware-Based | Firmware-based | Installed in device firmware, capturing keystrokes before the OS loads | Very High |
| Keyboard hardware keyloggers | Physical devices placed between keyboard and computer, recording all keystrokes | Medium (may be visible) | |
| Wireless keyboard sniffers | Intercept wireless signals between keyboard and receiver | Medium (requires specialized equipment) | |
| Keyboard overlays | Thin overlays placed on keyboards, capturing every key pressed | Low (easily visible) | |
| Acoustic keyloggers | Use sound sensors to capture the sounds of keystrokes | Low (detectable in quiet environments) | |
| Electromagnetic emissions | Capture electromagnetic radiation emitted during keystrokes (requires specialized equipment) | Very High | |
| Optical surveillance | Records video of users typing and uses computer vision to analyze keystrokes | Varies (depends on camera placement) | |
| Smartphones (with specific apps) | Malicious apps can be used to capture keystrokes on smartphones | Varies (depends on app and phone security) |
Keylogging in Research and Writing Process
Keylogging is used in various research fields, particularly to study writing processes. It helps researchers analyze:
- Speed and rhythm of typing;
- Pauses;
- Revisions;
- Other aspects of writing.
This provides insights into the cognitive and linguistic processes involved in writing.
Related Features and Supplementary Technologies
Keyloggers may have additional features that enhance functionality:
- Clipboard logging;
- Screen logging;
- Control text capture;
- Program and website monitoring;
- Capturing data from other input devices (mice, touchscreens);
- Capturing network traffic;
- Capturing audio recordings.
Countermeasures and Protection Against Keylogging
| Countermeasures and Protection Against Keylogging | Description |
|---|---|
| Anti-Keylogger Software | Software designed to detect and block keyloggers |
| Anti-Spyware/Anti-Virus Programs | Programs that detect and remove malicious software, including keyloggers |
| Network Monitors | Tools that monitor network traffic and block suspicious activity |
| Automatic Form Fillers | Software that automatically fills in login credentials and other sensitive information |
| Live CD/USB for Secure Booting | Booting from a trusted and secure operating system stored on a CD/USB drive |
| Security Tokens and One-Time Passwords (OTP) | Devices that generate unique codes for authentication |
| On-Screen Keyboards | Virtual keyboards that eliminate the need for physical keystrokes |
| Keystroke Interference Software | Software that generates random keystrokes or inserts additional characters |
| Speech Recognition and Handwriting Recognition | Alternative input methods that reduce the risk of keyloggers capturing keystrokes |
| Macro Expanders/Recorders | Software that automates repetitive tasks and reduces the need for manual typing |
| Deceptive Typing Techniques | Intentionally introducing errors or utilizing alternative keyboard layouts obfuscates keystrokes. This complicates keyloggers’ ability to intercept accurate data |
| Data Security and Privacy | Utilizing robust encryption methods for both storing and transmitting data collected through keyloggers is essential for safeguarding individuals’ privacy and maintaining data integrity |
Legal and Ethical Boundaries for Keylogger Usage
The use of keyloggers should be in compliance with legal regulations and ethical standards. Two main steps: to obtain an explicit consent from participants and to prioritize the secure handling of data. This helps to protect individuals’ privacy and maintain confidentiality throughout research and monitoring endeavors.
References
- Keystroke logging – Wikipedia
- What is a Keylogger? How to protect yourself
- What is a Keylogger? How to Detect a Keylogger?
- What is Keystroke Logging and Keyloggers?
- What is a Keylogger and How Can I Detect One on My Computer? | Sophos Home
- What is a keylogger? A total protection guide
- What is a Keylogger? A Detailed Guide | McAfee