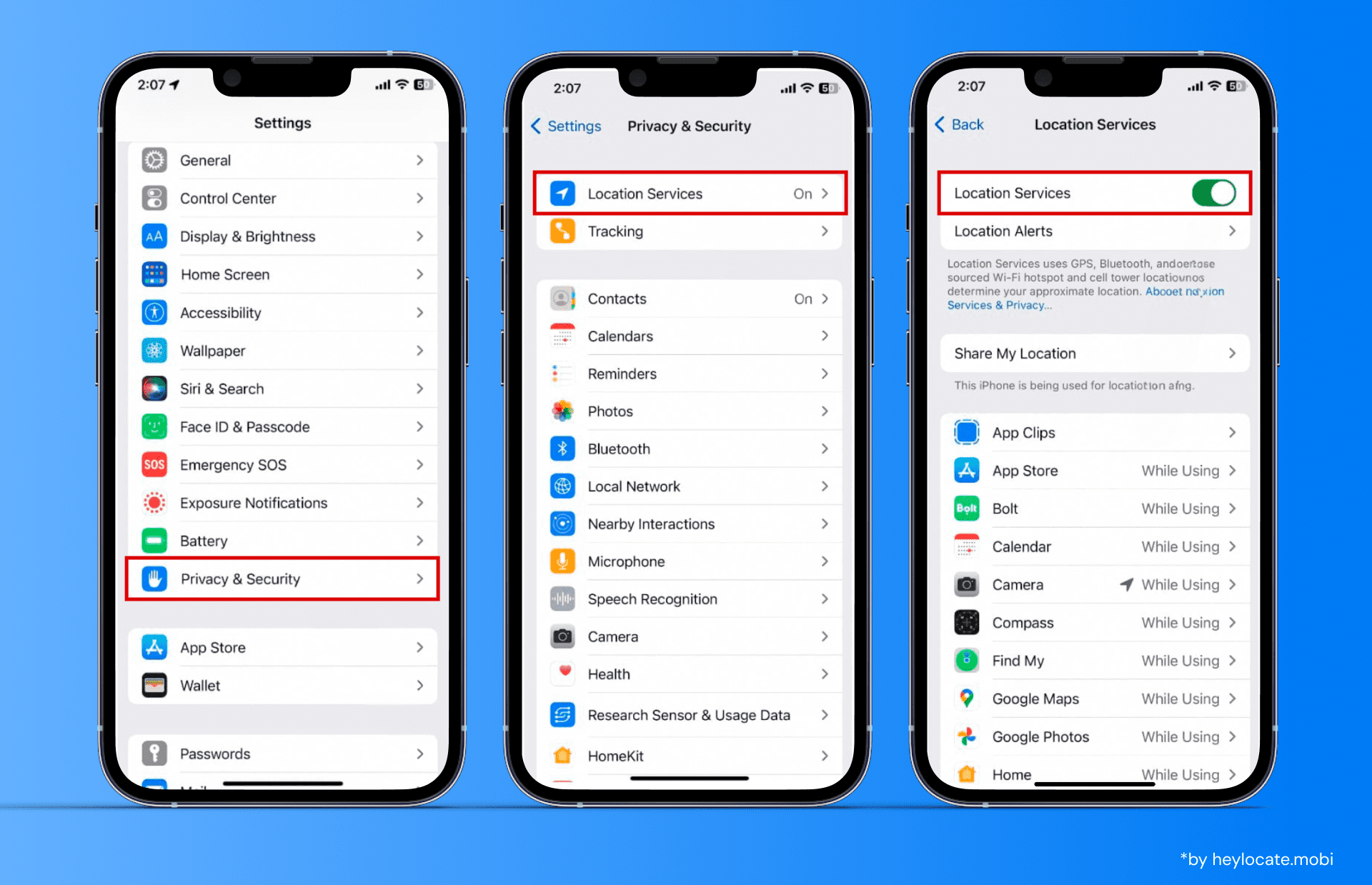
Location Services
What is Location Services?
Location Services, also known as Location-Based Services (LBS), is a technology that uses location data to provide relevant information and services to users based on their geographical position. This technology combines Global Positioning System (GPS), cellular networks, and mobile computing to determine and transmit location information. LBS have become an integral part of various applications and services, transforming how we navigate and interact with the world around us.
Importance and Applications of LBS in Various Domains
| Domain | Importance of LBS | Applications of LBS |
|---|---|---|
| Health | Enables remote monitoring, emergency assistance, and promotion of healthy lifestyles | Tracking patients’ locations, monitoring vitals, providing timely assistance during emergencies, and integrating with wearable devices and mobile applications to encourage physical activity and healthy living |
| Entertainment | Creates immersive experiences and personalized recommendations | Location-based games, augmented reality applications, and personalized recommendations for nearby attractions, restaurants, and events |
| Work | Improves efficiency and resource management | Location-based time tracking, resource allocation, asset management, route optimization, progress tracking, and providing relevant information on the go for field service professionals |
| Personal Life | Provides real-time, location-specific information and facilitates social connections | Finding directions, discovering nearby restaurants, social networking applications that connect users based on proximity, fostering new connections, and facilitating offline meetups |
Role of LBS in Business Insights and Government Operations
Business:
- Offers valuable insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and market trends.
- Utilizes product placement, targeted advertising, expansion strategies, and informed decision-making based on location data analysis.
Government:
- Enhances public services and operations through efficient management and planning.
- Implements emergency management systems, urban planning, traffic management, public transportation optimization, locating individuals in distress, and dispatching assistance promptly.
Networking and Communication:
- Enhances network efficiency, enables location-aware services, and ensures secure data transmission and storage.
- Implements location-based protocols for seamless communication between devices, encryption algorithms for secure data transmission, and data protection measures such as privacy policies and access controls.
Technical Foundations of LBS
Integration of GPS, cellular networks, and mobile computing for accurate positioning.
Location tracking methods:
- Control plane locating (using cellular towers).
- Emerging methods: Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and self-reported positioning.
LBS Privacy and Security Concerns
- Potential misuse of user location data revealing sensitive information.
- Legal frameworks and regulations to govern LBS and protect user privacy.
- Technical measures: anonymization, data minimization, and secure data transmission.
- User-centric LBS with control over location information sharing.
References
- Location-based service – Wikipedia
- location-based service (LBS) Techtarget
- What are Location-Based Services? Definition and FAQs | HEAVY.AI
- Location-Based Service – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- What are location-based services? | HPE Aruba Networking
- What are Location-Based Services (LBS)? – Definition from Techopedia