Triangulation
What is Cell Phone Triangulation?
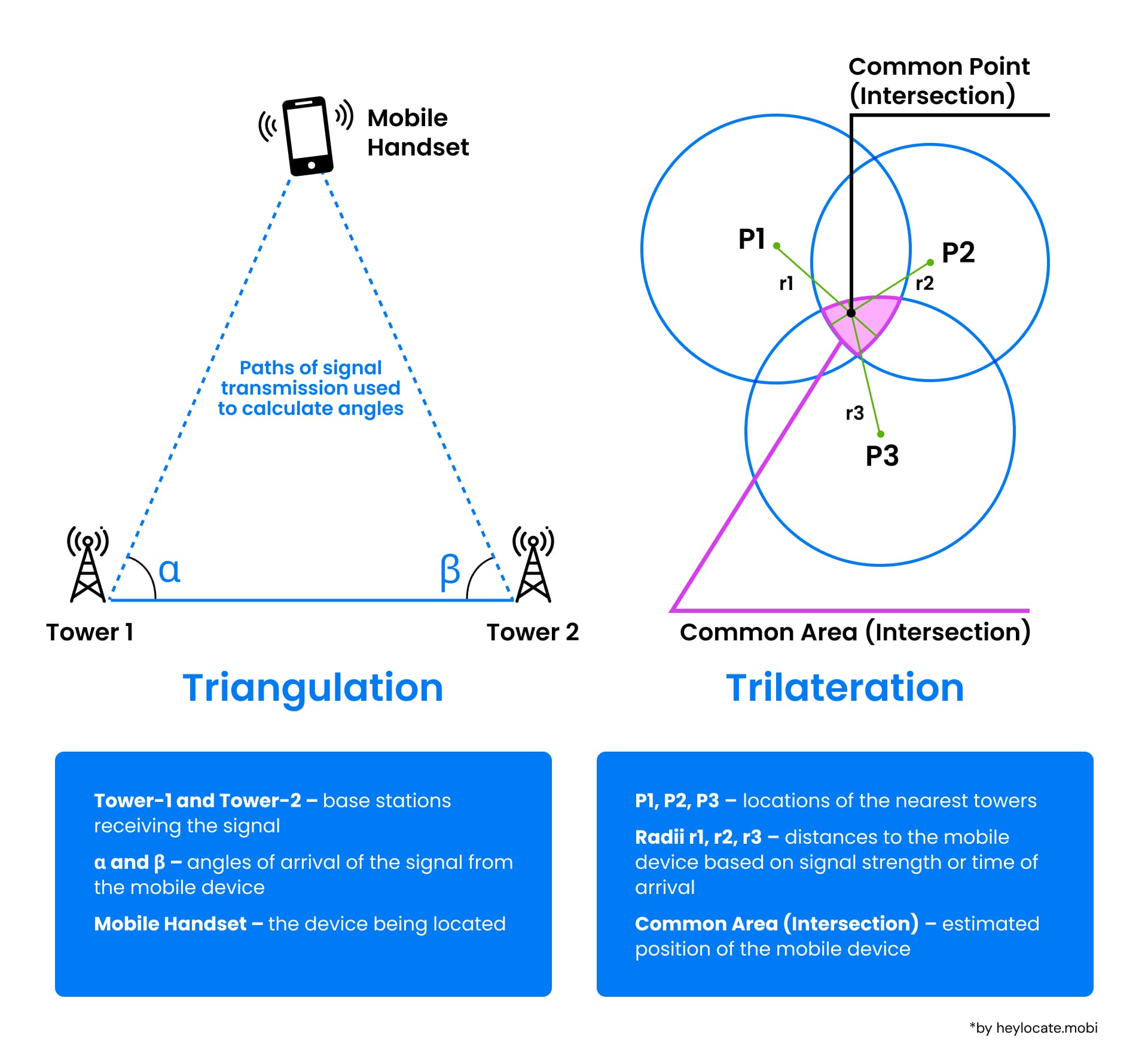
Cell phone triangulation is a technique used to determine the approximate location of a cell phone by analyzing the signals it exchanges with nearby cell towers. The term is also known as cell tower triangulation or mobile phone triangulation.
How does triangulation work?
Cell phone triangulation works by leveraging the geometry formed between the cell phone and cell towers around, using time or angular measurements to calculate the position of the phone within the network.
- Signal Interception by Cell Towers
When a cell phone gets a call or SMS, it sends and receives signals from nearby cell towers. For locating through triangulation, these signals should be picked up by at least three different towers within the network. - Measuring Time or Angle
To calculate the location, the time or angle of arrival of those cell phone signals are measured.
Time of Arrival (TOA) is the time it takes for a signal to go from the cell phone to each of the cell towers. Since the speed of signal travel is known, the cell phone location can be thus calculated.
Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) of signals at different towers can also help to determine the cell phone location.
Angle of Arrival (AOA) is the angle at which the signal from the cell phone arrives at each tower. By knowing these angles, the location of the cell phone can be pinpointed where these angles intersect.
Geometric principles or more complex algorithms like trilateration (using distances) or multilateration (using time differences) are applied to determine the precise location. The intersection of these measurements helps create a more accurate estimate of the phone’s location.
Accuracy of Triangulation
The accuracy of cell phone triangulation can be affected by factors such as the density of cell towers in the area and environmental variables like buildings or natural terrain that might obstruct signals. In practice, cell phone triangulation accuracy is:
- within about 50 to 100 meters in urban areas;
- from 100 to 500 meters in suburban areas;
- up to several kilometers in rural areas, where fewer cell towers exist.
Advanced algorithms can compensate for some inaccuracies by considering these factors and using additional data points or more sophisticated modeling techniques.
Applications in Telecommunications
Triangulation is crucial for enhancing the accuracy and reliability of communication systems. It is extensively used in various technologies, including mobile communication and satellite systems:
Mobile Communication
In mobile networks, triangulation helps determine the position of a mobile device based on the signal delay or angle of arrival of the signal from different cell towers. It is especially essential for services like emergency calls, where the caller’s location needs to be accurately and quickly determined.
Satellite Communication
For satellite-based systems, such as GPS, triangulation is employed to calculate a receiver’s exact location on Earth by measuring the time it takes for signals from multiple satellites to reach the receiver.
This method ensures precise navigation, timing, and positioning services, which are pivotal for various applications including aviation, maritime, and terrestrial navigation.
References
- Triangulation – Wikipedia
- Trilateration – Wikipedia
- Surveying – Wikipedia
- What is triangulation?
- Triangulation (geometry) – Wikipedia
- Triangulation – from Wolfram MathWorld
- Triangulation – Maple Help