Longitude
What is Longitude?
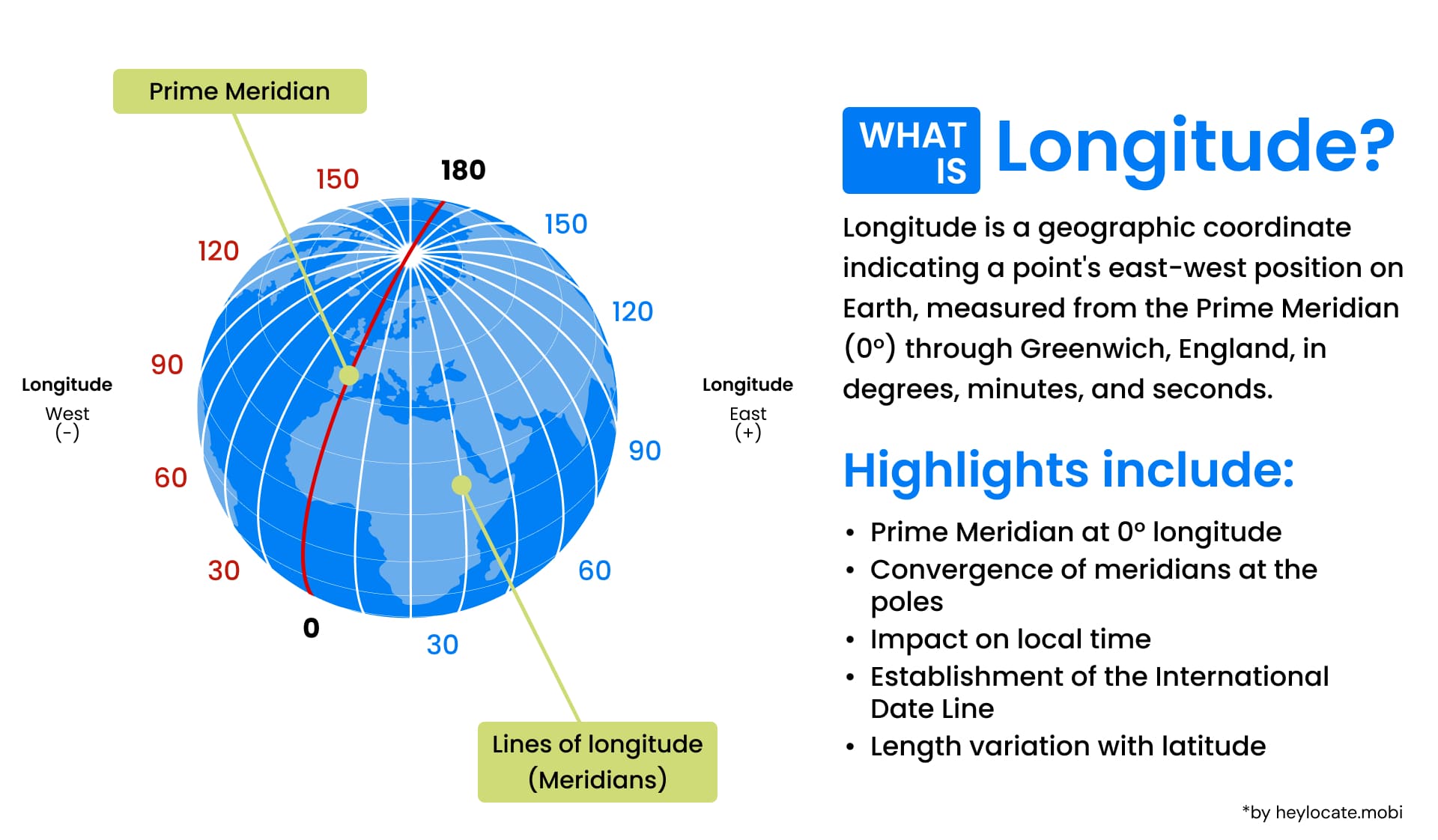
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth’s surface. It is one of the two coordinates used in the geographic coordinate system, with latitude being the other. Longitude is measured in degrees, with the Prime Meridian serving as the reference point for 0 degrees.
The Concept of Meridians and the Prime Meridian
Meridians are imaginary lines that run from the North Pole to the South Pole, connecting points of equal longitude. The Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, London, is the reference point from which all other longitudes are measured. It serves as the baseline for establishing time zones and is assigned a longitude of 0 degrees.
Representing Longitude in Degrees
Longitude is represented in degrees to quantify and compare the east-west position of different locations on the Earth’s surface. A full circle is divided into 360 degrees, with each degree representing 1/360th of the Earth’s circumference. By measuring the angle between the Prime Meridian and a given point, we can determine its longitude in degrees.
Longitude and Time Measurement
Longitude and time measurement are intricately connected. The Earth rotates 360 degrees in approximately 24 hours, which means it rotates by 15 degrees per hour. This relationship allows us to use time to determine longitude. By comparing the local time at a specific location with the time at the Prime Meridian (Greenwich Mean Time), we can calculate the longitudinal difference and, consequently, the longitude.
Related Concepts and Measurements
To fully understand longitude, it is essential to consider its relationship with latitude. Latitude measures the north-south position of a point on the Earth’s surface, while longitude measures the east-west position. Together, they form a grid that allows for precise positioning and navigation.
Latitude is measured in degrees, similar to longitude. The equator serves as the reference point for latitude, with 0 degrees representing the equator and 90 degrees representing the North and South Poles.
Length of a Degree of Longitude
The distance represented by a degree of longitude varies depending on latitude. Due to the Earth’s slightly oblate shape, the distance between meridians decreases as you move closer to the poles. At the equator, a degree of longitude is approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles). This distance reduces towards the poles, reaching zero at the North and South Poles.
References
- Longitude – Wikipedia
- What is longitude? Noaa.gov
- Longitude | National Geographic
- What is longitude? | Royal Museums Greenwich
- Longitude | Definition & Examples – Lesson | Study.com
- What is Longitude? – WorldAtlas