Dark Web
What is Dark Web?
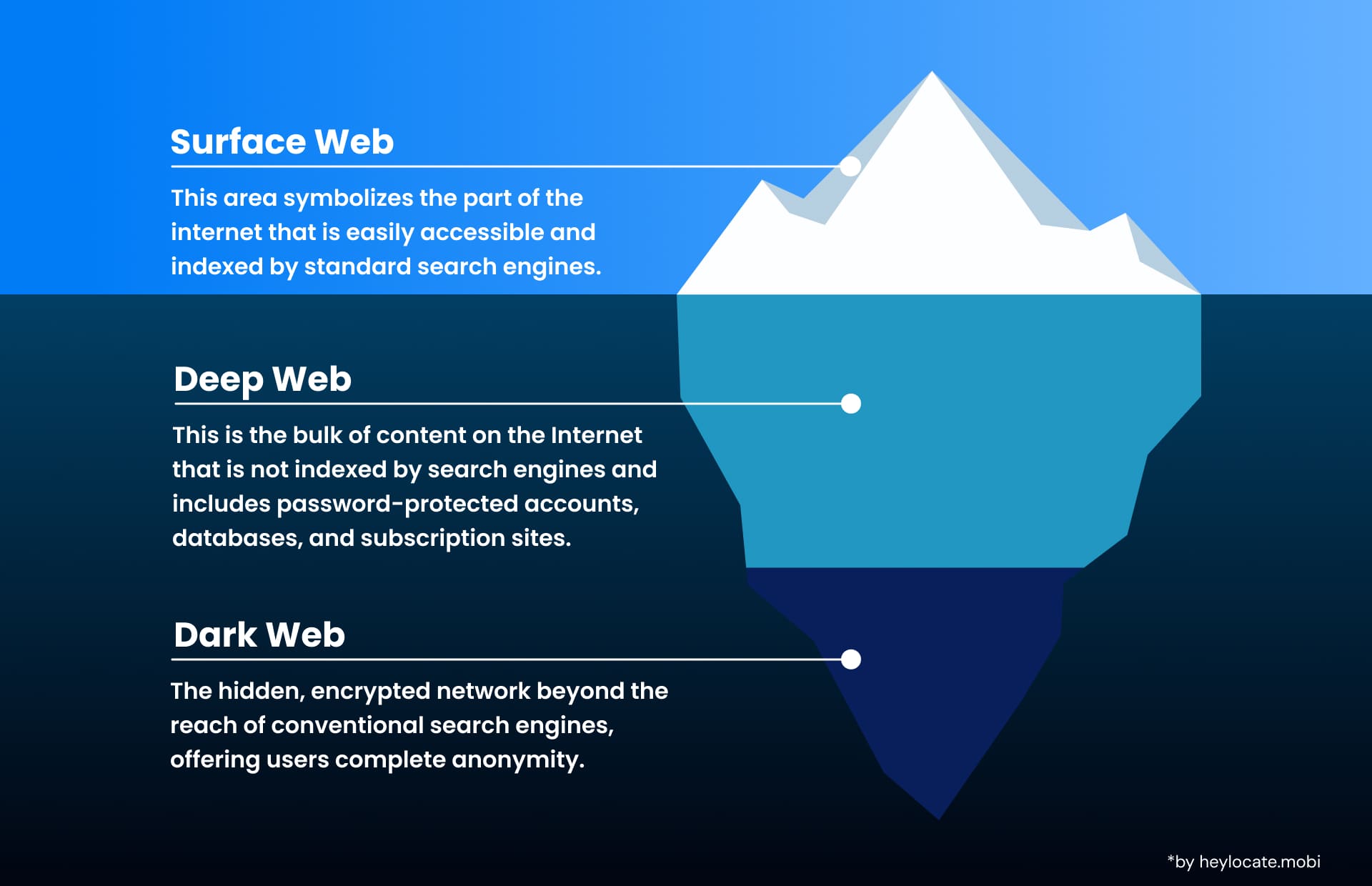
The Dark Web is a section of the deep web that requires special tools, configurations, or authorization. It is this part of the internet that is deliberately obscured and is not discovered by standard web browsers. In contrast to the deep web, which contains all web pages not indexed by search engines, such as password-protected pages or subscription-based content, the dark web is characterized by anonymity and decentralization.
Technological Foundations
The dark web is based on some technical foundations, such as the Tor anonymity network. Tor, an open-source software, anonymizes internet browsing by bouncing traffic through interconnected relays operated by volunteers and encrypting data at each step. Through this process, the user’s IP address is masked, making it impossible for the online activities to be traced.
Besides Tor, other overlay networks such as Freenet and I2P provide anonymous communication for dark web users. Freenet is an anonymous and censorship-resistant anonymizer, while I2P is a secure and private communication layer for applications. Riffle is also a system providing a high level of anonymity guarantees.
Dark Web Terminology
While “dark web” and “deep web” are frequently put the same way, noticing their differences is essential. The deep web includes all web pages not indexed by search engines; the dark web, on the other hand, is a part of the deep web that cannot be accessed without special software or with authentication.
The dark web is usually accessed through the Tor network and its onion routing. The Tor protocol encrypts internet traffic and routes it through a series of Tor nodes, which makes it untraceable to the person behind it. Dark web sites commonly have .onion domain names indicating they exist on the Tor network.
Ensuring Anonymity and Security
The dark web can achieve anonymity through encryption methods like end-to-end encryption, which makes it impossible for third parties to intercept a message and decipher its content, as only the sender and intended recipient can access it.
The VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) also create a secure encrypted tunnel between a user’s device and the internet. This ensures that the user’s IP address and location are concealed. On the other hand, the dark web’s uneven regulation gives rise to a high possibility of fraud, viruses, and other cybersecurity threats.
Types of content on the Dark Web
The dark web has a vast array of content that may be legal or illegal. Some authentic services and content examples are anonymous forums, whistleblower platforms, and privacy-oriented applications. On the one side, it can be a frequent place for illegal activities like trading drugs, weapons, stolen data, hacking services, fake documents, and other debatable information.
Users should take precautions while browsing the dark web and comprehend the legal and moral consequences. Law enforcement agencies monitor and investigate criminal activities on such platforms.
References
- “Going Dark: The Internet Behind The Internet”. NPR. 25 May 2014.
- Greenberg, Andy (19 November 2014). “Hacker Lexicon: What Is the Dark Web?”. Wired.
- “Clearing Up Confusion – Deep Web vs. Dark Web”. BrightPlanet. 2014-03-27.
- Dark web – Wikipedia
- What is the Deep and Dark Web?
- What is the dark web and how do you access it? – Norton