Bluetooth
What is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is a close-range communication and data-transmission protocol that allows wireless communications between various electronic devices. It applies the 2.4GHz frequency band and transfers data over radio waves in both directions (transmission and receiving).
Bluetooth was first created to replace physical connections between devices, such as mobile phones, laptops, and peripherals. It enables the transmission of many types of data (for example, speech, video, and text) over large areas. Bluetooth wireless technology allows devices with Bluetooth to connect without having to use cables or have complicated procedures set up.
The main advantages of the Bluetooth protocol include:
- Low-power consumption: therefore, it is perfect for devices working on wireless batteries like smartphones, tablets, and headphones.
- Capability to create PANs (Personal Area Networks) to link multiple devices. This enables the user to use the phone as the remote control for speakers, smart TV, or any other Bluetooth-equipped device by choosing among the connected devices.
Technical Specifications
Bluetooth uses the 2.4 GHz ISM band and frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) techniques that help deal with interference. It has a transmission power of up to 100 milliwatts, a range of about 100m (330ft).
Bluetooth is a support technology with 79 channels with a bandwidth of 1 MHz each. The bandwidth ranges from 1 Mbps (Bluetooth 1. x) to 3 Mbps (Bluetooth 2.0+EDR and latest versions). Standard Bluetooth at version 5.0 delivers high-speed data set, long-range transmission, and interference minimization.
Management and Standards
The Bluetooth SIG (Special Interest Group), an industry consortium of several companies from the telecommunication, computing, and consumer electronics sectors, is the body that manages the Bluetooth standard.
SIG manages the development and promotion of Bluetooth technology, providing interoperability and compatibility with other Bluetooth devices. They determine the technical specifications and requirements for Bluetooth devices, which should follow a common set of technical standards. This will enable heterogeneous devices from different vendors to communicate with each other without barriers.
The SIG further manages the Bluetooth trademark and licensing program, so companies could use the Bluetooth mark and logo on their products to indicate their adherence to the Bluetooth standard. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) also assists in standardizing Bluetooth by standardizing the physical and media access control (MAC) layers for Bluetooth communication through the IEEE 802.15.1 standard. This standardization ensures that Bluetooth devices can work properly and operate with other wireless technologies that use the same frequency bands.
Bluetooth Origin
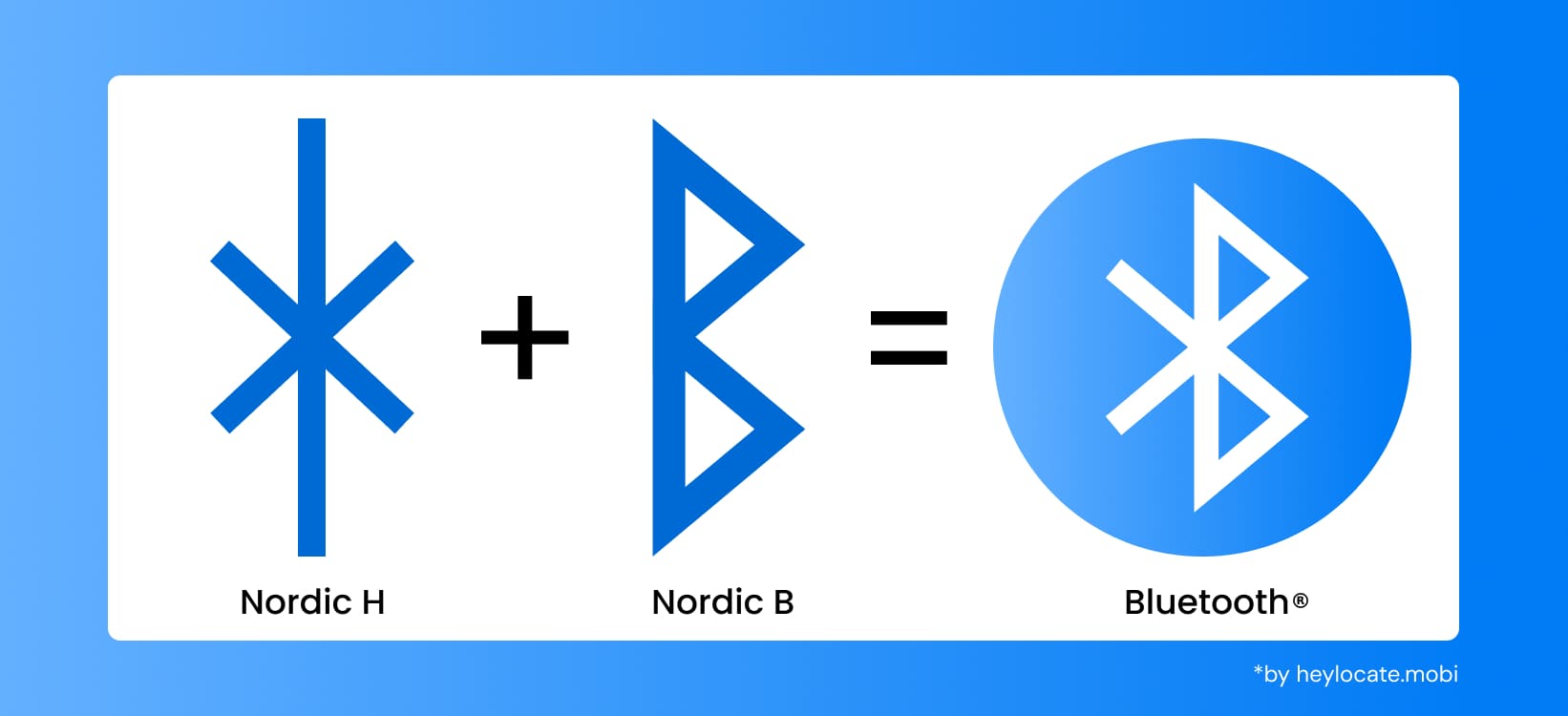
The word “Bluetooth” is actually the literal translation of the name of the Scandinavian king, Harald Blåtand (Bluetooth), who, in the 10th century, reputedly brought together rival factions within the Nordic countries. The name is derived from Harald Bluetooth, a Danish king, the dominant ruler of the 10th century. The main traits that made Harald Bluetooth stand out from other monarchs were his effective diplomacy and communication within different tribes. The name was picked to reveal what this technology does – connecting various devices and operations in the industrial industry and elsewhere.
Development and Adoption
The implementation of Bluetooth technology began late in the nineties when Ericsson, a Finnish telecom company, chiefly concentrated on eliminating the cables used in communication gadgets. Ericsson did the same just a year later, in 1998, when it formed a consortium of companies, including Nokia, IBM, and Intel, and Bluetooth Special Interest Group (B-SIG) was given the job of advancing and promoting the technology. The SIG is comprised of members from top Bluetooth technology companies, and together, they work on developing new Bluetooth technologies.
The practicality of Bluetooth replaced its competitor, infrared technology, in the early 2000s, representing one of the most distinctive eras of mobile phone history. This was marked by the introduction of low-energy wireless devices such as mobile phones, laptops, and wireless headsets. These devices became a basis for many consumer electronic products, enabling seamless connectivity and data transfer between devices.
Expansion and Standardization
With the growing success of Bluetooth, the Bluetooth SIG performed a vital task of developing and bringing novel Bluetooth applications to the realization, as well as guaranteeing device compatibility by fine-tuning the Bluetooth standard.
Bluetooth headsets provided the initial focus. However, the technology gradually expanded into many consumer electronics products, such as mobile phones, laptops, speakers, smartwatches, and home automation systems. This broadened the scope of possibilities for wireless connectivity and gave birth to technological innovation in the consumer electronics market.
Standardization was the key to Bluetooth success, with the Bluetooth SIG and the IEEE jointly defining technological specifications and requirements, which provided unified principles for all devices irrespective of their brands or models.
Notable Milestones
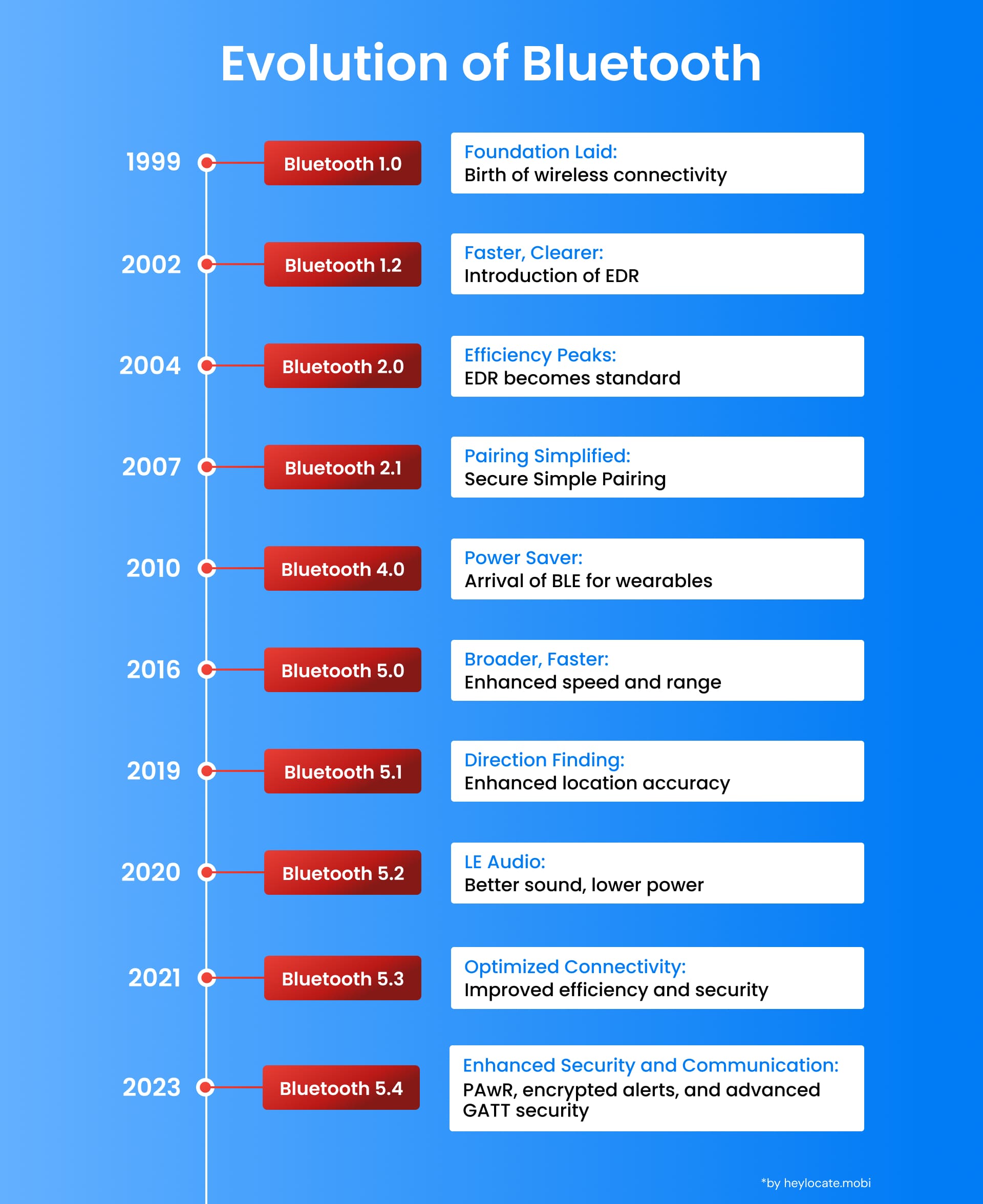
Notable Milestones in Bluetooth Development:
- 1999: The Bluetooth 1.0 Specification was introduced, thus paving the way for Bluetooth devices’ connectivity.
- 2002: Bluetooth profile 1.2 added ULtra high-speed Data Rate (EDR) Technology to speed up data transfer and improve audio quality.
- 2004: Under the Bluetooth 2.0 Specification, Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3, which represent support for better speeds and power efficiency, were made available as standard features.
- 2007: Bluetooth 2.1 specification provided SSP (Simple Secure Pairing) for better security and managed pairing.
- 2010: The Bluetooth 4.0 Specification brought in Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology for device families like fitness trackers and smartwatches requiring low-power connections.
- 2016: Release 5.0 of Bluetooth specifications was characterized by better features, which included higher data rate speed, longer range, and better sharing with other Wi-Fi Technologies.
These milestones attest to the Bluetooth technology’s unceasing development and modernization that turned into new applications and enlarged wireless connection ecosystems.
References
- “Bluetooth Range: 100m, 1km, or 10km?”. bluair.pl.
- “Basics | Bluetooth Technology Website”. Bluetooth.com. 23 May 2010.
- Muller, Nathan J. (2002). Networking A to Z. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 45–47.
- “About us – Bluetooth Technology Website”. Bluetooth.com.
- “Brand Enforcement Program“. Bluetooth.com.
- Bluetooth SIG – Specifications: Specifications | Bluetooth® Technology Website
- Wikipedia – Bluetooth: Bluetooth – Wikipedia
- IEEE Xplore – Overview of the Bluetooth Technology: Bluetooth technology | IEEE Conference Publication