Reverse Geocoding
What is Reverse Geocoding?
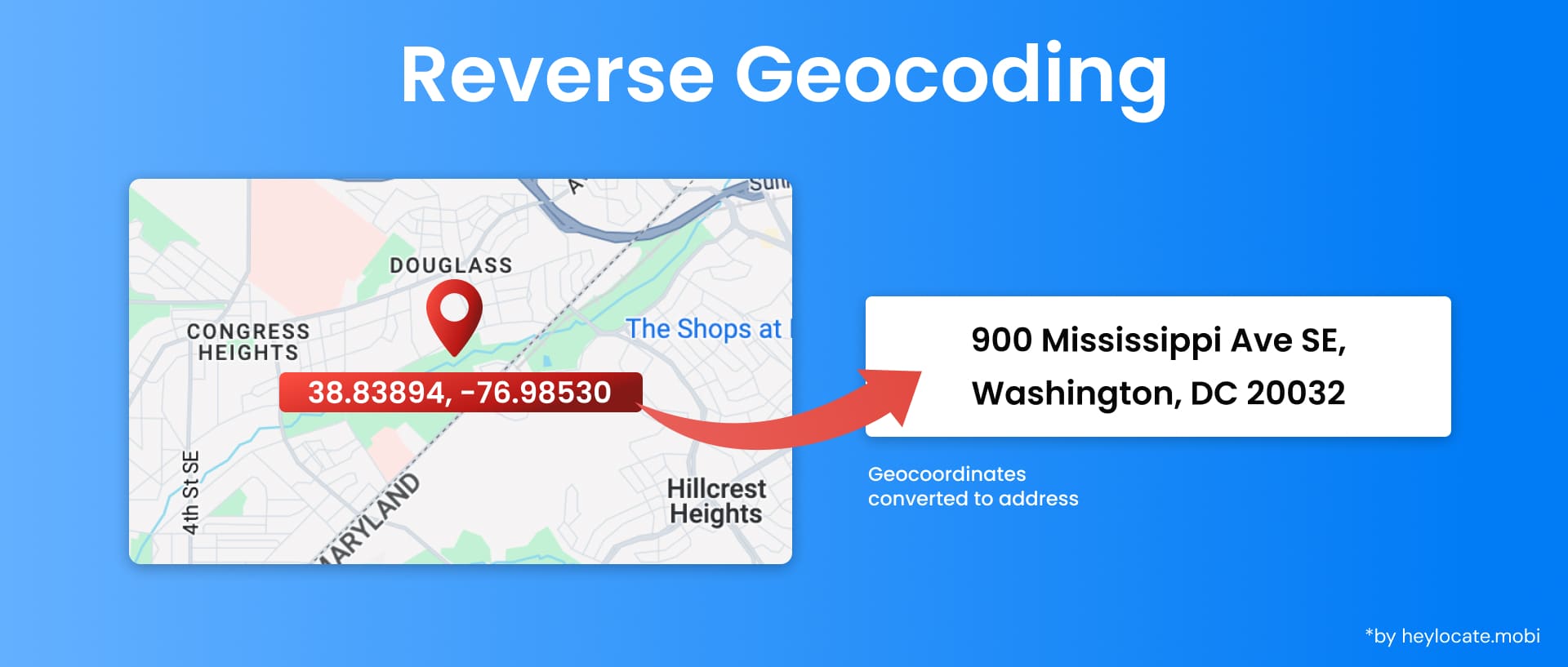
Reverse geocoding is a process that transforms geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) into a human-readable address. It is the opposite of forward geocoding, which converts addresses into coordinates. Reverse geocoding identifies the closest address or location associated with a given pair of coordinates, utilizing a vast and continuously updated database of addresses and locations.
Applications and Importance
| Navigation and Mapping | Enables navigation systems and mapping applications to provide users with relevant information about nearby addresses, landmarks, or points of interest based on input coordinates |
| Emergency Response | During emergencies, reverse geocoding helps emergency services pinpoint the location of a caller by converting coordinates from a distress call into an address, facilitating a faster response |
| Location-Based Services | Underpins various location-based services like ride-hailing apps, delivery services, and social media check-ins |
| Research and Analysis | Aids in research and analysis by enabling the conversion of spatial data (coordinates) into meaningful addresses for better understanding and visualization |
| Urban Planning and Environmental Monitoring | Plays a role in urban planning and environmental monitoring by facilitating spatial data analysis associated with specific locations |
How Reverse Geocoding Works
Reverse geocoding follows a systematic approach:
- Collect and organize vast address data based on geographic regions, including street names, house numbers, and postal codes.
- Identify the nearest known point or feature (street segment, intersection, or landmark) from the inputted coordinates.
- Interpolation of the address based on available address data for that location involves determining the closest street address or intersection and estimating the house number according to proximity to known addresses.
Interactive and GIS-Based Methods
- Interactive maps allow users to click on a map point and retrieve the associated address, benefiting casual users who need occasional address lookup.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) enable georeferencing techniques to match coordinates with addresses, providing greater precision and flexibility for reverse geocoding.
Reverse Geocoding Services and APIs
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| GeoNames | Offers a comprehensive database and continuous updates for reverse geocoding |
| Google Maps Platform | Provides a wide range of geocoding and reverse geocoding services, including geocoding, place search, and distance matrix calculations |
| OpenStreetMap | A collaborative mapping project that provides open and high-quality geographic data |
Privacy Implications of Reverse Geocoding
- Opt-out mechanisms can be implemented to allow users to prevent their coordinates from being converted into addresses, which is particularly relevant for individuals who wish to keep their locations confidential.
- Differential privacy techniques can be employed to add noise or generalize reverse geocoding results, protecting individual privacy but requiring a balance to maintain usefulness.
References
- Reverse geocoding – Wikipedia
- Reverse geocoding (address lookup) request and response | Google Maps Platform, Guides: Documentation – Web Services
- Introduction to Reverse Geocoding
- Reverse Geocoding | What it is and how to do it
- Fundamentals of reverse geocoding – ArcGIS Pro
- What is Reverse Geocoding? Latitude and Longitude to Address
- What is Reverse Geocoding – Converting Coordinates to Address | Melissa