Data Roaming
What is Data Roaming?
Data roaming is the capability provided by wireless telecommunications networks that enable mobile users to maintain connectivity and access mobile data services when outside the geographical coverage area of their home network. It ensures uninterrupted access to mobile data services by allowing users to connect to mobile networks beyond their home network’s coverage zone, employing sophisticated mobility management techniques.
To facilitate data roaming, various procedures are involved, including mobility management and authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA). When a user roams onto a visited network, their identity and credentials must undergo verification and authentication to ascertain they possess the requisite permissions to access the network’s data services. Typically, the user’s home network oversees this authentication process, communicating with the visited network to establish the user’s credentials and billing information, facilitating seamless data roaming experiences.
Forms of Roaming
Roaming encompasses two primary forms: SIM-based and username/password-based roaming. SIM-based roaming, the predominant form, utilizes information stored on the user’s SIM card to authenticate and authorize their access to a visited network. Conversely, username/password-based roaming necessitates the user’s manual entry of credentials to establish a network connection.
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) plays a crucial role in SIM-based roaming. GSM roaming facilitates users’ worldwide connectivity to diverse GSM networks, ensuring seamless compatibility and interoperability across networks. Conversely, WLAN roaming enables users to seamlessly transition between various Wi-Fi networks while moving between access points. Both forms of roaming are geared towards furnishing uninterrupted access to mobile data services, enhancing user experience and connectivity reliability.
| Feature | SIM-Based Roaming | Username/Password-Based Roaming |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Uses SIM card for automatic authentication | Requires manual entry of username and password |
| Ease of Use | Connects automatically to networks | User must manually connect to each network |
| Mobility | Typically offers broader international coverage | May be limited to specific networks or regions |
| Security | Embedded security features in SIM card | Depends on the strength of the user’s password and the network’s security protocols |
| User Experience | Seamless transition between networks | Potentially less seamless as it may require re-authentication |
| Compatibility | Dependent on GSM standards, widely adopted | May vary depending on the network’s supported authentication methods |
| Billing | Charges are typically billed through the home network provider | May require separate billing or payment methods for access |
| Setup | Requires a roaming agreement between network operators | Can be used with Wi-Fi and other networks that accept credentials |
Roaming Agreements
Roaming agreements form the bedrock of roaming services, establishing the terms, conditions, and legal and business frameworks governing partnerships between mobile network operators. The GSM Association, a global trade association representing mobile network operators, furnishes guidelines and recommendations for crafting these agreements.
Negotiating roaming partnerships entails thorough discussions and consensus on various aspects, including pricing, interconnection, and revenue distribution. Mobile network operators strive to guarantee seamless roaming experiences for their customers across different networks, mitigating excessive charges. Additionally, these agreements delineate technical specifications, encompassing signaling protocols and data exchange formats, to uphold network interoperability standards.
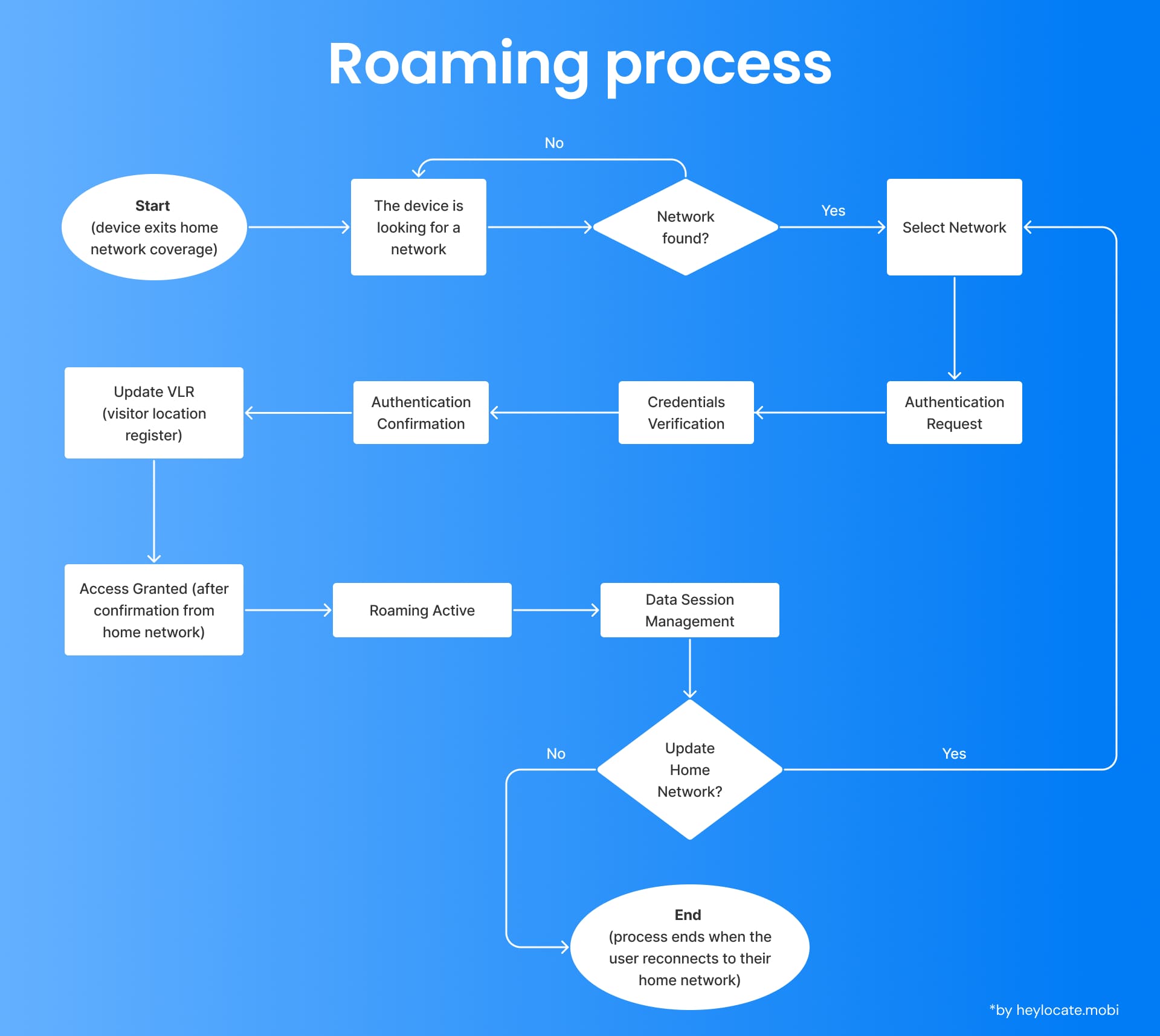
The Roaming Process
The roaming process encompasses several technical steps to facilitate a seamless user transition. As users move from their home network’s coverage area to a visited network, their mobile device initiates a location update to notify the home network of the new location. This update includes pertinent information, such as the user’s current cell ID and network ID, facilitating accurate tracking. Subsequently, the home network updates its visitor location register (VLR) with this information, ensuring updated records of the user’s whereabouts.
Moreover, the roaming process entails the management of mobile-terminated data sessions. When attempts are made to communicate with a roaming user, the data is directed to the home network, which then collaborates with the visited network to establish a connection and deliver the data to the roaming user’s device. This necessitates seamless coordination and cooperation between multiple networks to ensure the successful transmission of data.
International Roaming
Concerns over data charges for travelers have historically accompanied international roaming. However, concerted efforts have been undertaken to mitigate or eradicate these charges. International agreements forged between countries or regions seek to cultivate a conducive environment for roaming, allowing users to access mobile data services without facing exorbitant expenses.
For instance, the European Union (EU) has enacted regulations to reduce roaming charges within its member states. These regulations establish ceilings on roaming charges, curbing excessive fees associated with data usage while traversing EU borders. Analogous agreements and initiatives are prevalent in other global regions, aiming to render roaming more cost-effective and accessible for users worldwide.
References
- “Steering of Roaming Implementation Guidelines” (PDF). GSM Association.
- European Union Roaming Regulations
- Roaming – Wikipedia
- What is Data Roaming? A Guide to Managing Cellular Data Usage | T-Mobile
- What is Data Roaming? | Xfinity
- What is Data Roaming: A Comprehensive Guide | Gigsky