Indoor Positioning System (IPS)
What is IPS?
An Indoor Positioning System (IPS) is a system designed to ascertain the location of individuals or objects within buildings and other indoor environments. Unlike Global Positioning System (GPS), which often proves ineffective indoors due to signal blockage, IPS leverages various technologies to offer precise positioning information.
Technologies and Techniques Behind IPS
Indoor Positioning Systems employ various technologies and techniques to achieve accurate positioning within indoor spaces. These include:
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Wi-Fi-Based Positioning System (WPS) | Utilizes existing WiFi infrastructure within a building to determine the location of devices |
| Bluetooth | Creates a network of reference points using beacons or tags for accurate positioning |
| Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GNSS | Achieves centimeter-level accuracy by utilizing correction data from reference stations |
| Acoustic Signals | Calculates position based on the time it takes for ultrasonic or audio signals to reach different sensors |
| Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) | Combines data from accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers to estimate position and orientation |
| Ultra-Wideband (UWB) | Provides precise positioning by using low-energy, short-duration pulses across a wide frequency band |
| Magnetic Positioning | Utilizes the Earth’s magnetic field or local magnetic anomalies to determine position and orientation |
| Computer Vision | Processes images or video streams to extract positioning information from visual features |
| Light-Based Positioning | Uses light sources (e.g., LEDs) and receivers to estimate position based on light signal characteristics |
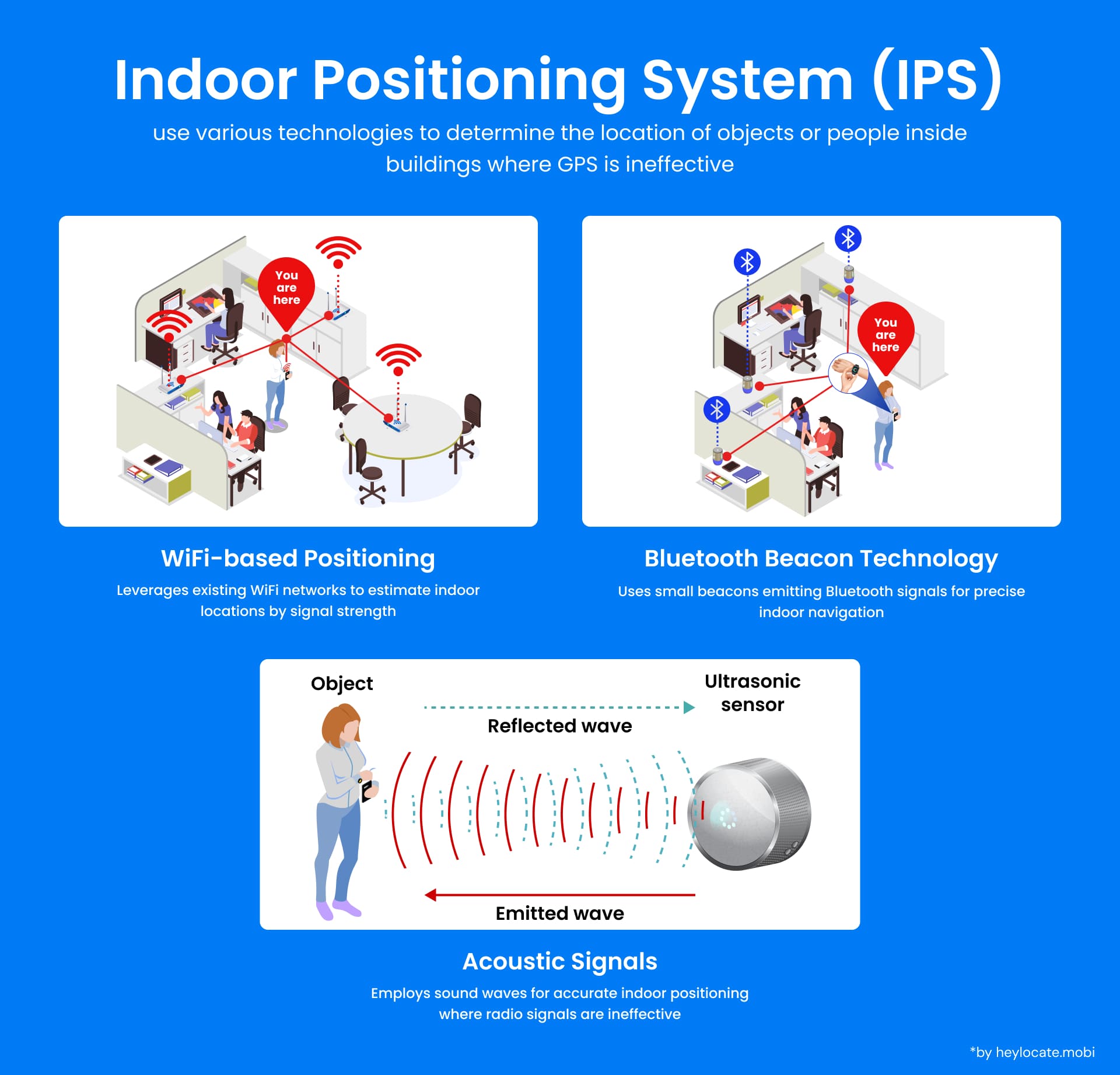
How Does IPS Work?
IPS installations typically comprise a network of sensors or beacons strategically positioned within a building. These sensors may either be purpose-built devices specifically engineered for positioning or existing infrastructure components such as WiFi access points or Bluetooth beacons.
The precision of IPS is attained through a variety of techniques, including the utilization of Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers. These receivers leverage correction data from reference stations to achieve centimeter-level accuracy.
Achieving High Accuracy
To improve accuracy, IPS systems can:
- Deploy a dense network of beacons or sensors within a building.
- Employ advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze data from multiple sensors.
- Integrate data from other systems, such as motion sensors or inertial measurement units (IMUs), to compensate for errors caused by factors like device orientation or signal interference.
Applications of IPS
| Application Sector | Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Commercial | Personalized shopping experiences Location-based promotions Optimized store layouts |
| Healthcare | Tracking medical equipment Monitoring patients and staff Improving efficiency and patient care |
| Military | Enhancing situational awareness Improving the safety of personnel Coordinating and executing operations |
| Logistics and Manufacturing | Optimizing workflows Tracking inventory Improving overall efficiency |
Integration with Other Systems
| Service | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems | Improved accuracy and additional contextual information for indoor navigation |
| Internet of Things (IoT) devices | Real-time information about occupancy, environmental conditions, and asset tracking |
References
- Farid, Z.; Nordin, R.; Ismail, M. (2013). “Recent Advances in Wireless Indoor Localization Techniques and System”. Journal of Computer Networks and Communications. 2013: 1–12
- “2cm accuracy using an Indoor Positioning System”. VBOX Automotive.
- Indoor positioning system – Wikipedia
- Indoor Navigation vs Indoor Positioning by Mappedin
- Indoor Positioning Systems & Location Tracking (Indoor GPS) | Inpixon
- Indoor Positioning System & Location Tracking Types | Litum