Real-time Locating System (RTLS)
What is RTLS?
The Real-time Locating System (RTLS) is a technology used to track the location of objects or people in real time within confined areas. It provides accurate and up-to-date information about the position and movement of assets, enabling organizations to improve efficiency, enhance safety, and streamline operations.
Components of an RTLS
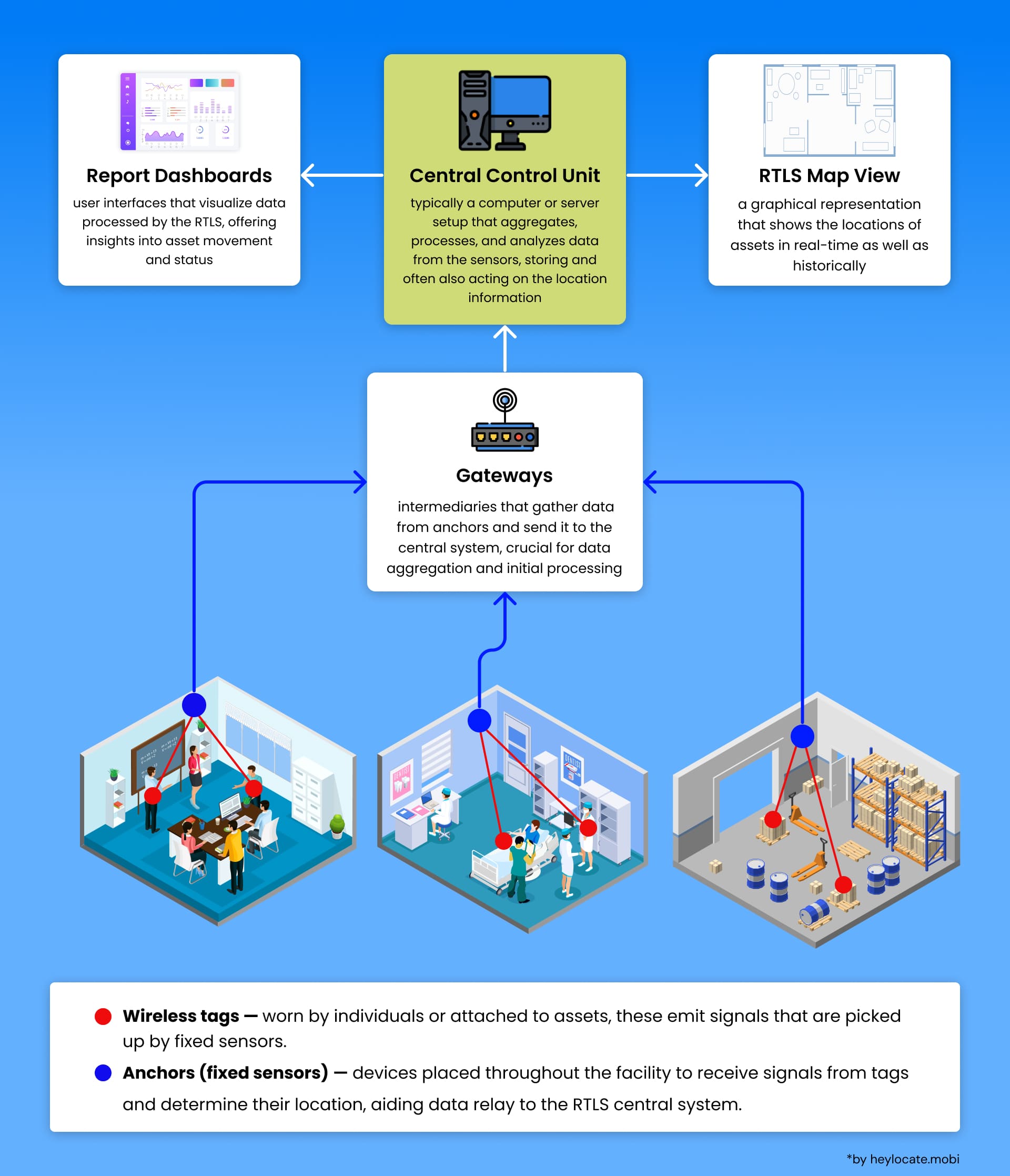
An RTLS typically consists of three key components:
- Wireless tags: Also known as transponders or beacons, these are attached to the objects or worn by individuals. They emit signals that are received by fixed reference points.
- Fixed reference points: These are strategically placed throughout the area and equipped with technologies like radio frequency (RF), optical, or acoustic systems to triangulate the position of the tags.
- Tracking technologies: These technologies determine the location of the tags using the signals they emit.
Locating Techniques
RTLS employs two primary approaches for locating objects or people: choke point locating and locating in relative coordinates.
- Choke point locating: This method involves placing reference points at specific entry or exit points to create virtual checkpoints. The location of a tagged object or person is recorded and updated in real time when passing through these checkpoints.
- Locating in relative coordinates: This approach utilizes trilateration or triangulation techniques to determine the precise location of an object or person.
Technologies Used in RTLS
- Active RFID: It uses radio frequency identification (RFID) tags that emit signals at regular intervals, enabling real-time location tracking.
- Infrared: It uses infrared light to communicate between the tags and reference points, allowing for accurate location tracking.
- Ultrasonic: It uses sound waves to determine the location of tagged objects or people by analyzing signals received and analyzed by reference points.
- Ultra-wideband (UWB): Employs brief, minimally consumptive energy impulses to convey data between the tags and reference points, presenting a notable level of precision and accuracy.
Practical Applications of RTLS
| Industry | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Equipment Tracking | Track medical equipment to improve response times |
| Workflow Optimization | Monitor staff to streamline processes | |
| Patient Safety Enhancement | Reduce infection risks and prevent patient elopement | |
| Logistics & Operations | Asset Management | Track assets to improve utilization and reduce losses |
| Staffing Levels Optimization | Monitor employee movement to enhance productivity | |
| Process Improvement | Analyze workflow to enhance efficiency |
Privacy Concerns with RTLS
The application of Real-Time Location Systems for individual tracking elicits privacy considerations, including consent, data security, and the potential misuse of location information. It is imperative that organizations adopt transparent data acquisition methods and establish robust privacy protections.
Limitations and Challenges of RTLS
- Line of sight: Some technologies require a clear line of sight for accurate tracking.
- False locations: Signal reflections can cause inaccurate location data.
- Real-time data accuracy: Maintaining accuracy in dynamic environments can be challenging.
- Interference with medical equipment: Potential for RF-based systems to interfere with medical devices in healthcare settings.
References
- Real-time locating system – Wikipedia
- What Is RTLS? | An Overview of Real-Time Locating Systems | Zebra
- What Is RTLS Technology? (Real-Time Location Systems)
- What are Real Time Location Systems in Healthcare?
- RTLS | pozyx.io
- What is RTLS – Real Time Location System? | Litum
- What is RTLS: Real Time Locating Systems? – WIPELOT