Ultra-wideband (UWB)
What is Ultra-Wideband (UWB)?
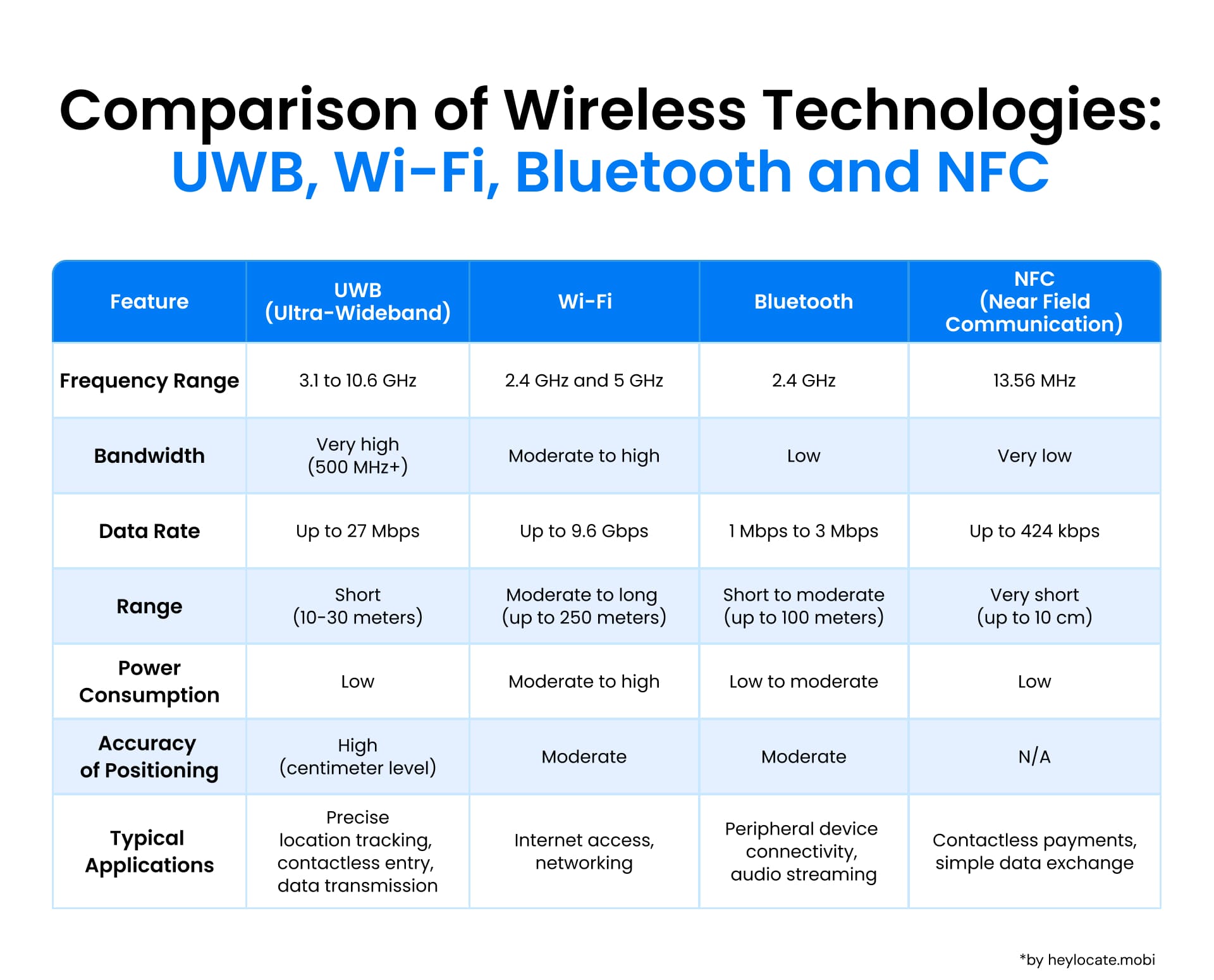
Ultra-wideband (UWB) is a wireless communication technology that allows short-range, high-bandwidth communications with low-energy usage. It is characterized by its ability to transmit information across a wide bandwidth, utilizing a large portion of the radio spectrum to transmit data. This wide bandwidth allows for high-data-rate communications without interference, enabling various industry applications.
Key Characteristics of Ultra-wideband Technology
- Wide Bandwidth Transmission: UWB transmits data using short-duration pulses spread across a large frequency range. This wide bandwidth allows for high-data-rate communication and reduces interference from other wireless technologies.
- Regulatory and Efficient Use: UWB operates within specific power levels and frequency ranges set by regulatory bodies. This efficient use of radio bandwidth enables precise positioning and low-latency communication.
Theoretical Aspects of UWB Technology
- Conventional vs. UWB Radio Transmissions: Unlike conventional narrowband transmissions using carrier waves, UWB transmits data using ultra-short pulses across a wide frequency range, making it resistant to interference.
- Time of Flight and Multipath Propagation: UWB utilizes time-of-flight techniques to measure the travel time of signals between devices, enabling precise positioning and mitigating multipath propagation effects.
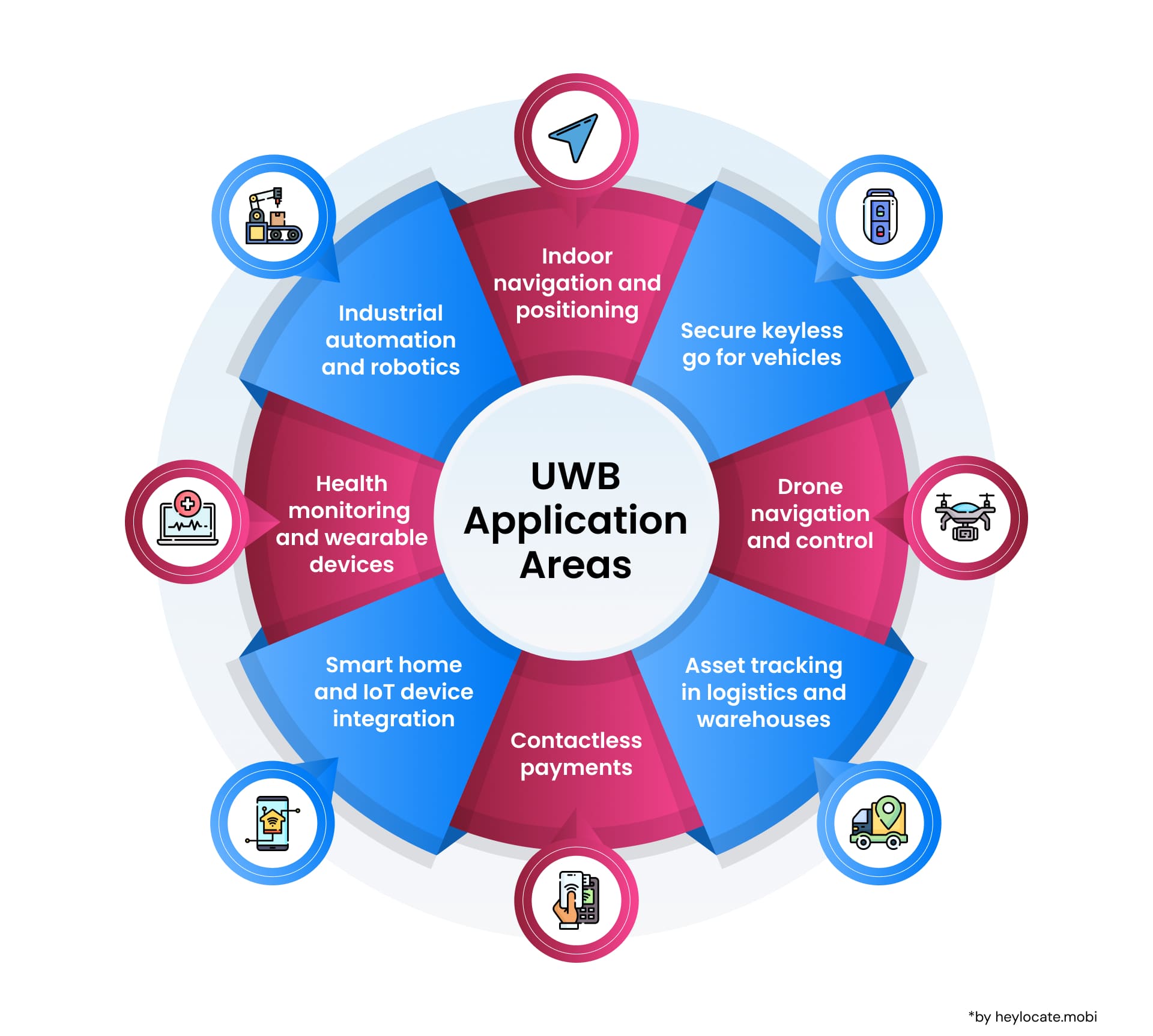
Applications of Ultra-wideband Technology
| Application Area | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Location Services | Precise indoor and outdoor positioning of objects and individuals | Asset tracking, indoor navigation, proximity-based services |
| Mobile Devices | Enhanced functionalities through precise positioning | Spatial audio, AR applications, seamless device pairing |
| Industrial Applications | Improved automation, robotics, worker safety, and asset tracking | Manufacturing process monitoring, location-based safety systems, real-time asset tracking |
| Radar and Monitoring | Object detection, security, vital sign monitoring, “see-through-the-wall” imaging | Security surveillance, automotive radar, contactless health monitoring, search and rescue operations |
| Autonomous Vehicles | High-bandwidth data transfer, precise localization, V2I, and V2V communication | Sensor data transmission, real-time decision-making, vehicle-to-infrastructure communication for traffic updates, vehicle-to-vehicle communication for collision avoidance |
Ultra-Wideband Products and Chips
The market for UWB products and chips has been growing steadily since the introduction of UWB technology in smartphones. Various suppliers offer UWB products and chips that cater to different applications and requirements.
| Product Name | Standard | Band | Announcement Date | Commercial Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product A | UWB 1.0 | 6 GHz | May 2020 | Asset Tracking |
| Product B | UWB 2.0 | 8 GHz | July 2019 | Real-time Locationing |
| Product C | UWB 1.5 | 4 GHz | March 2021 | Autonomous Vehicles |
| Product D | UWB 2.0 | 6 GHz | January 2020 | Industrial Automation |
References
- Ultra-wideband – Wikipedia
- How does ultra-wideband work? By Samsung
- What Is Ultra-wideband (UWB) Wireless Communication? | Murata Manufacturing Articles
- What is Ultra-Wideband (UWB)? Here’s everything you need to know | Bleesk
- What is Ultra-wideband? A guide to UWB technology – Antenova
- Ultra-Wideband Positioning & Sensors (UWB RTLS) | Inpixon
- What is UWB, and why is it in my phone? Ultra wideband technology, explained